Canada is the most multicultural nation on earth
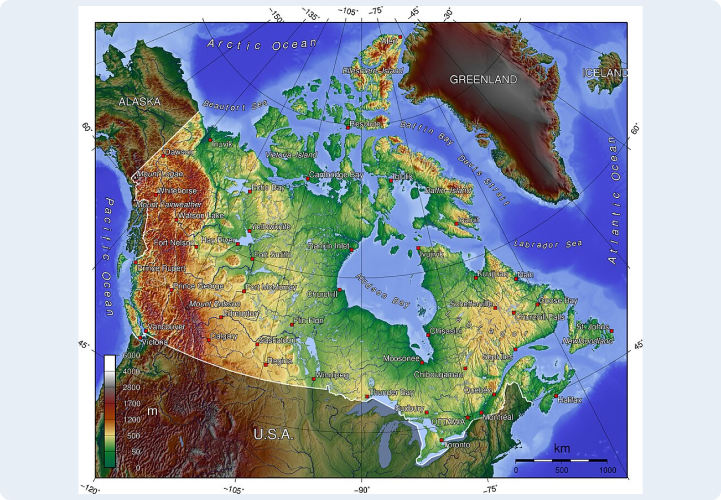

Canada is the most multicultural nation on earth. Its landmass covers almost 10 million square kilometers, from the Shiny Atlantic to the Mighty Pacific. Ironically, the name Canada derives from the word Kanata, which in the Iroquoian language means, “Village.” Indeed, Canada is a giant and diverse “Global Village.”
Here are a few key facts about Canada:
1. Geography:
- Provinces and Territories: Canada is divided into 10 provinces and 3 territories.
- Provinces: Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, and Saskatchewan.
- Territories: Northwest Territories, Nunavut, and Yukon.
- The country features diverse landscapes, from the Rocky Mountains and Prairies to vast forests, Arctic tundra, and thousands of lakes.
2. Capital and Major Cities:
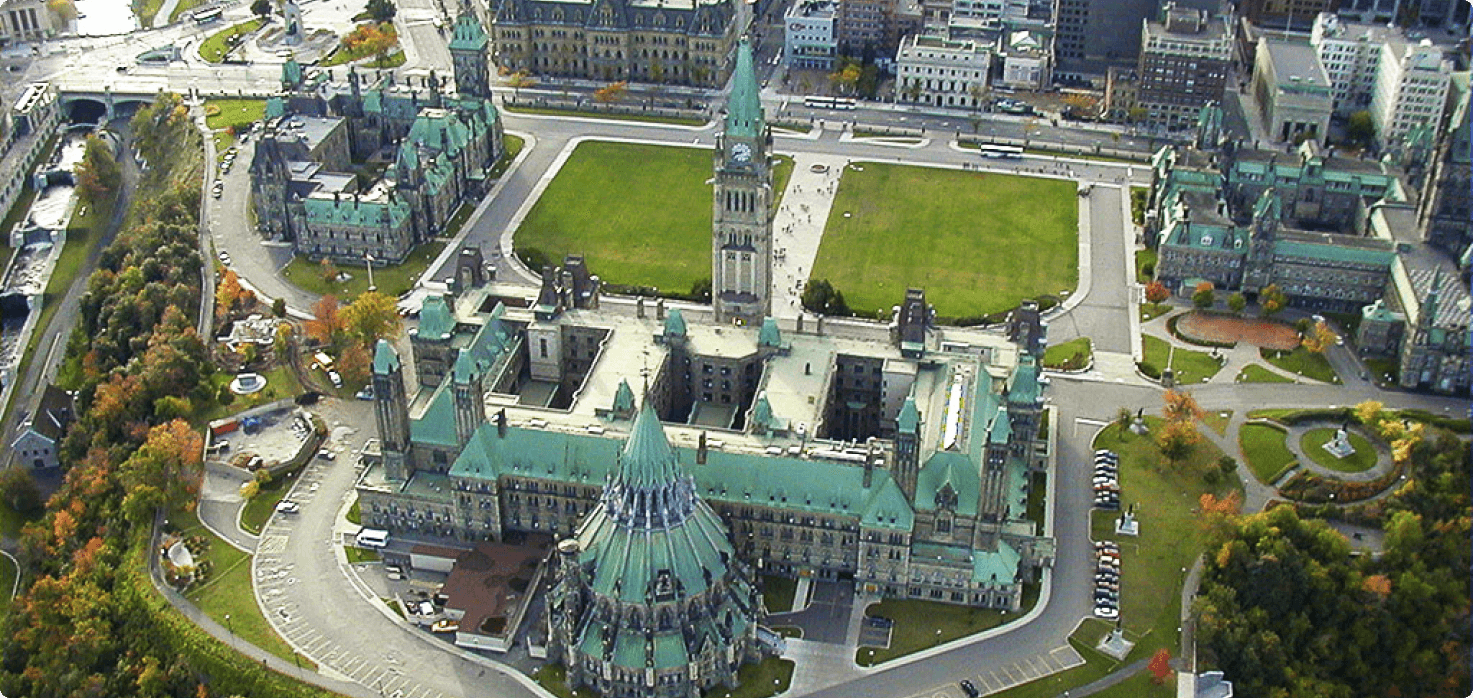
- Capital: Ottawa (in Ontario).
- Other major cities include Toronto (the largest city), Vancouver, Montreal, Calgary, Edmonton, and Quebec City.
3. Language:
- Canada has two official languages: English and French.
- Other major cities include Toronto (the largest city), Vancouver, Montreal, Calgary, Edmonton, and Quebec City.
4. Climate:
- The climate varies widely, from arctic conditions in the north to temperate in the south. Winters can be long and harsh, especially in the central and northern parts, while coastal areas, like British Columbia, have milder winters.
5. Culture:
- Canada is a multicultural society, with a long history of immigration. It is known for its inclusive policies, strong social safety nets, and commitment to human rights.
- Indigenous peoples: The country is home to diverse Indigenous cultures, including First Nations, Inuit, and Métis, whose histories and contributions are integral to Canadian identity.
6. Economy:
- Canada has a highly developed and diverse economy, with strengths in natural resources, technology, manufacturing, and services.
- Major industries include oil and gas, forestry, mining, automotive manufacturing, and technology (especially in cities like Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver).
7. Government:
- Canada is a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy. The monarch (currently Queen Elizabeth II’s successor) is the ceremonial head of state, while the Prime Minister is the head of government.
- The country has a strong tradition of peacekeeping and diplomacy on the international stage.
8. Sports:
- Hockey is Canada’s most popular and iconic sport, but other sports like lacrosse, Canadian football, and soccer also have significant followings.
- The country has a strong presence in the Winter Olympics and has hosted the Games multiple times (e.g., Vancouver 2010).
IMMIGRATION TO CANADA
Immigrating to Canada is a rewarding experience, and there are several pathways to make Mighty Canada Your Sweet Little Home. Here is a brief overview of Canada’s main immigration programs:
1. Express Entry System (for Skilled Workers)
The Express Entry system is one of the fastest ways for skilled workers to immigrate to Canada. It’s a points-based system where you are ranked according to your age, work experience, education, language proficiency, and adaptability…
2. Provincial Nominee Program (PNP)
Each province in Canada has its own PNP, allowing them to nominate individuals who have the skills needed. You can apply to a PNP directly or through Express Entry (if eligible).
3. Family Sponsorship
If you have a family member who is a Canadian citizen or permanent resident, they may be able to sponsor you for permanent residency.
4. Educational Permits (Pathway to Permanent Residency)
Many people come to Canada as international students and later transition to permanent residency.
5. Startup Visa Program (for Entrepreneurs)
If you are an entrepreneur with a viable and innovative business concept, which can create jobs for Canadians, you can apply for a Startup Visa.
6. Work Permit
If you get a job offer from a qualifying Canadian employer, you can apply for a temporary work permit. Certain categories of workers, like skilled workers or intra-company transferees, may also qualify for work permits.
7. Atlantic Immigration Program (AIP)
If you want to live and work in one of Canada’s four Atlantic provinces (Newfoundland and Labrador, Prince Edward Island, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick), you can apply through the AIP. It’s designed for skilled workers and international graduates.
8. Temporary Resident Visa (TRV)
A Temporary Resident Visa (TRV) is required for individuals who want to visit Canada for tourism, business, or family visits.
9. Refugee, Asylum/Humanitarian Programs:
If you’re fleeing persecution, war, or violence, you may be eligible for refugee status in Canada. This process is different from other immigration programs and is based on humanitarian grounds.
As you can see there are a multitude of programs for proper immigration to Canada. Of course, each option has its own specific eligibility requirements and delicate nuances. Navigating through this complex process can be daunting. Fortunately, Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers have a wealth of professional experience to help you turn your Immigration Dreams into Realities Safely and Soundly.
WHAT ARE THE ESSENTIAL IMMIGRATION STEPS TO CANADA?
Here are the essential steps for Canadian Immigration:
1. Eligibility
The best path to Canada depends on various factors such as age, education, work skills, experience, family ties, language proficiency and so on. The main pathways are:
2. Documentation:
Once you’ve chosen the appropriate immigration path, you will need to gather the required documents. Common documents include:
- Proof of identity (passport, birth certificate)
- Educational credentials (degree certificates, transcripts)
- Proof of work experience (reference letters, job contracts)
- Language proficiency
- Police certificates and medical exams (for security clearance)
- Proof of funds (showing you can support yourself and any dependents)
3. Language Testing
For most immigration pathways, you will need to demonstrate your proficiency in English or French. Accepted tests include:
- IELTS (International English Language Testing System)
- CELPIP (Canadian English Language Proficiency Index Program)
- TEF (Test d’évaluation de français)
Language skills are assessed based on your ability to read, write, listen, and speak. The higher your score, the more points you earn for your application, especially under the Express Entry system.
4. Submit Your Application
Once you have prepared your documents and completed the necessary tests, you can submit your application. If you are applying through Express Entry, you must join the Express Entry pool. If you’re applying through another pathway, such as family sponsorship or a work permit, you can apply directly.
5. Wait for a Decision
After submitting your application, you’ll need to wait for a decision from Canadian immigration authorities. The processing time varies depending on the type of application:
- Express Entry: A few months (typically 6 months or less)
- Provincial Nominee Program (PNP): Can take several months
- Family Sponsorship: Usually about 12 months
You may be asked for additional documents or information during the processing time.
6. Receive Your Invitation to Apply (ITA)
If applying through Express Entry and you meet the points threshold (based on your profile), you may receive an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residence. Once you receive an ITA, you must submit your complete application for permanent residency within 60 days.
7. Complete Medical and Security Checks
You will undergo medical exams to ensure you meet the required health standards. A police clearance certificate may also be required to verify that you have no criminal record.
8. Receive Your Visa
If your application is approved, you will be issued a visa to travel to Canada. After arriving, you’ll be a permanent resident, and you’ll receive a Permanent Resident (PR) card.
9. Prepare for Life in Canada
Settlement Services: After arrival, many settlement services are available to welcome you into Canadian society, and help you find a place to live, take language courses, etc.
Health Insurance: Once you’re a permanent resident, you’ll be eligible for provincial health care programs, which may vary by province.
Social Services: Learn about Canada’s social services, taxation, and other programs that may assist you in your new home.
In summary, immigration to Canada is shaped by both federal and provincial laws, with the federal government setting the broad framework for immigration, including economic, family, and refugee programs, while provincial and territorial governments, through programs like the Provincial Nominee Program (PNP) and specific regional initiatives, play a vital role in addressing local labor market needs and demographic goals. The combination of these laws and programs allows for a more flexible, regionally focused immigration system that aims to benefit both Immigrants and Canada. If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
CANADIAN IMMIGRATION BY CHOICE OF PROVINCE
ONTARIO



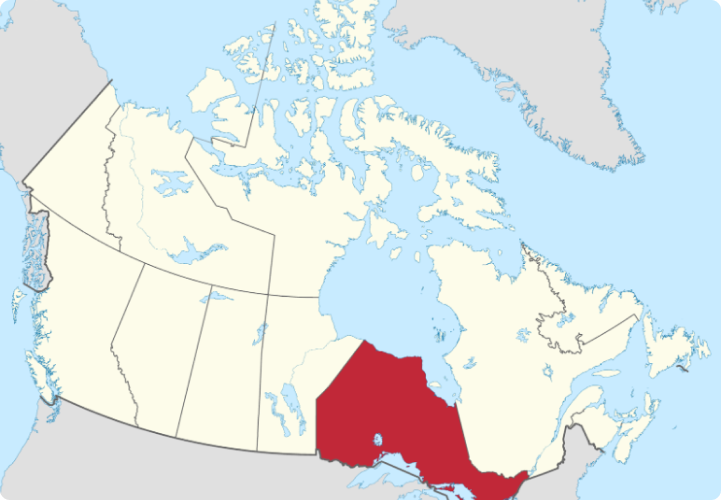
With approximately 15.7 million inhabitants or about 40% of the entire Canadian Population, Ontario is Canada’s most Populous Province; and it is growing fast, due to high birth rate and immigration.
The name Ontario is derived from Indigenous Peoples’ languages, and it means “Great Lakes,” “Beautiful Water,” or “Sparkling Water.” Indeed, all such names represent this colossal Province, which has about 250,000 freshwater lakes. Ontario is one of Canada’s 10 provinces, located in the central part of the country. It’s the most populous province and home to major cities like Toronto (Canada’s largest city) and Ottawa (the national capital). Here’s a brief overview of Ontario:
1. Geography
- Ontario is bordered by Manitoba to the west, Quebec to the east, the U.S. states of New York, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Minnesota to the south, and the Hudson Bay to the north.
- The province is home to vast forests, lakes, and rivers, including Lake Ontario, Lake Erie, Lake Huron, and parts of Lake Superior.
2. Climate
- Ontario experiences a humid continental climate, with cold winters and warm summers. The southern part of the province has a more temperate climate, while the northern areas can have much harsher winters.
3. Economy
- Ontario has a highly diversified economy, with industries including manufacturing, finance, technology, agriculture, and natural resources.
- Toronto is the financial hub of Canada, housing the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSE).
- The province is also a significant contributor to Canada’s auto manufacturing, mining, and forest industries.
4. Culture and Population
- Ontario has a population of around 15 million people (as of 2023), which makes up roughly 40% of Canada’s total population.
- The province is a multicultural hub, with large communities of immigrants from all over the world. Toronto is one of the most culturally diverse cities globally.
5. Tourism and Attractions
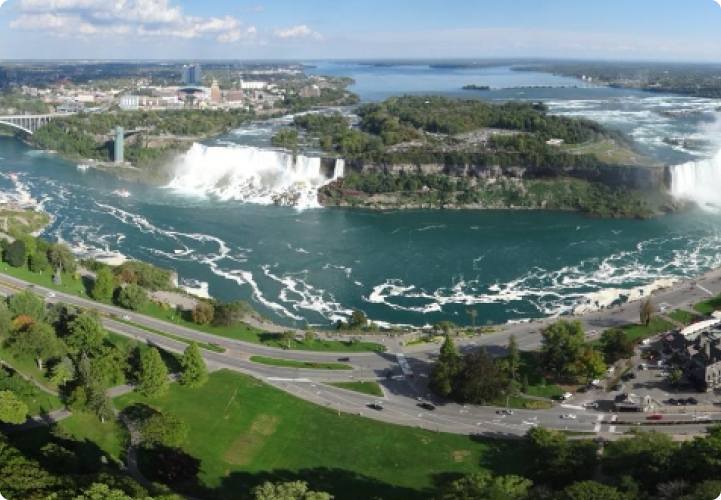
- Niagara Falls is one of the most famous natural attractions, drawing millions of visitors annually.
- Algonquin Provincial Park, located to the north, is a popular destination for outdoor activities like hiking, canoeing, and wildlife watching.
- Toronto offers a range of attractions including the CN Tower, the Royal Ontario Museum (ROM), and the Distillery District.
- Ottawa, Canada’s capital, features iconic landmarks like Parliament Hill, Rideau Canal, and the National Gallery of Canada.
6. Politics
- Ontario is a provincial government under Canada’s federal system. It has a Premier (the head of government) and a Lieutenant Governor (the representative of the Queen).
- The current Premier (as of 2023) is Doug Ford, leader of the Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario.
- The province has a provincial parliament located in Queen’s Park, Toronto.
7. Education
- Ontario is home to some of Canada’s top universities, such as the University of Toronto, McMaster University, and Queen’s University.
- It has a publicly funded education system from kindergarten to high school, as well as a large network of colleges and vocational schools.
8. Transportation
- Ontario has a well-developed transportation network, including major highways like Highway 401 (the busiest highway in North America) and Highway 400.
- The Toronto Pearson International Airport is Canada’s busiest airport.
- Ontario also has extensive public transit systems, particularly in Toronto with the TTC (Toronto Transit Commission), including subways, buses, and streetcars.
Ontario is a key player in Canada’s economy and cultural landscape, making it a vibrant, dynamic, and important region in the country.
TORONTO
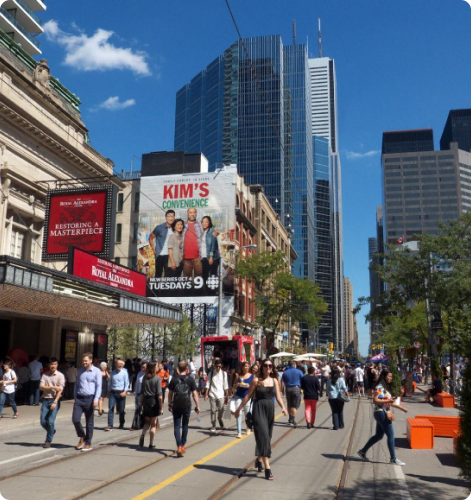
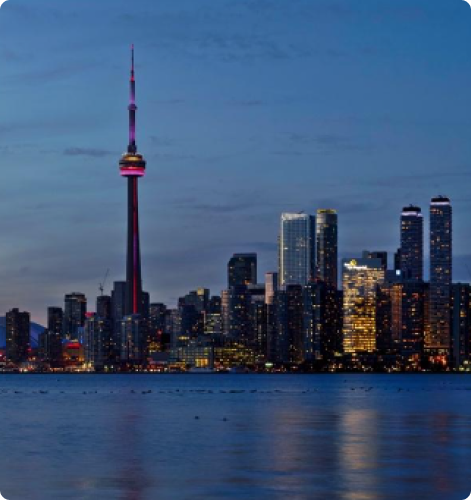



With a combined population of about 10 million people, the greater metropolitan and surrounding neighborhoods, Toronto is indeed a unique testament to peaceful co-existence. The diverse population of Toronto reflects its current and historical role as an important destination for Immigrants. About half of its residents are born outside of Canada and over 200 ethnic origins are represented among its inhabitants. While the majority of Torontonians speak English as their primary language, over 160 languages are spoken in the city.
Key Highlights of Toronto:
- CN Tower: Once the tallest freestanding structure in the world, the CN Tower offers breathtaking views of the city and Lake Ontario. Visitors can also enjoy the revolving restaurant at the top.
- Royal Ontario Museum (ROM): One of the largest museums in North America, with vast collections in art, culture, and nature.
- Toronto Islands: A group of small islands located just off the shore of downtown Toronto, offering beaches, parks, and a serene escape from the city hustle.
- Distillery District: A historic area with cobblestone streets, galleries, shops, and restaurants, showcasing Victorian-era buildings that were once part of a distillery.
- St. Lawrence Market: A world-famous market with fresh produce, meats, cheeses, and unique artisanal goods.
- Kensington Market: A diverse neighborhood known for its bohemian atmosphere, vintage shops, and international food.
- Toronto Raptors: The city’s NBA team, winner of the 2019 championship.
- Toronto International Film Festival (TIFF): One of the most prestigious film festivals in the world, attracting major stars and filmmakers.
- 032099
Neighborhoods:
- Downtown Toronto: The heart of the city, where you’ll find the business district, entertainment venues, and the majority of the city’s skyscrapers.
- Queen Street West: Known for its vibrant arts scene, eclectic shops, and trendy cafes.
- Yorkville: Upscale shopping, high-end dining, and art galleries.
- The Annex: A bohemian neighborhood with a mix of students, young professionals, and creative types.
Weather:
Toronto experiences a variety of weather. Winters can be cold, with temperatures often dipping below freezing, while summers are generally warm, with temperatures averaging in the mid-20s°C (70s°F). Snowfall is common in winter, though Toronto doesn’t see as much as some other Canadian cities, like Montreal or Winnipeg. Toronto is a thriving center for music, theater, motion picture, and television production. Toronto is also home to the Toronto Stock Exchange, five of the Largest Canadian Banks, and many Large Canadian and Multinational Corporations.
Toronto is the third-largest tech hub in North America after New York and California.
ONTARIO IMMIGRATION PROGRAMS
Ontario offers its immigration programs through the Ontario Immigrant Nominee Program (OINP). The key categories under OINP include:
a. Employer Job Offer Stream
- Foreign Worker Stream: For individuals with a job offer from an Ontario employer in a skilled position (NOC 0, A, or B).
- International Student Stream: For international students who have completed their education in Ontario and have a job offer.
- In-Demand Skills Stream: For workers with job offers in specific high-demand sectors such as construction, agriculture, or hospitality.
b. Human Capital Stream
- Human Capital Priorities Stream: For skilled workers with experience in occupations in demand in Ontario, including those with a profile in the Express Entry system.
- French-Speaking Skilled Worker Stream: For bilingual French-English speakers with experience in eligible occupations.
- Skilled Trades Stream: For skilled tradespeople who are qualified in Ontario’s labor market.
c. Business Immigration
- Ontario Business Stream: For individuals who wish to establish, operate, or buy a business in Ontario.
- Corporate Stream: For international corporations looking to establish or expand their operations in Ontario
d. Express Entry Human Capital Priorities Stream
- Ontario selects candidates from the Federal Express Entry pool who have the required skills and experience to work and live in Ontario.
2. Federal Immigration Pathways
In addition to provincial programs, there are several federal immigration options available for those wanting to immigrate to Ontario:
a. Express Entry
- Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP): For individuals with skilled work experience, education, and language skills.
- Federal Skilled Trades Program (FSTP): For workers in skilled trades.
- Canadian Experience Class (CEC): For individuals who have worked in Canada and want to transition to permanent residence.
b. Family Sponsorship
- Citizens and permanent residents of Canada can sponsor their close family members, including spouses, common-law partners, dependent children, parents, and grandparents, for immigration to Ontario.
c. Atlantic Immigration Program
- For individuals with job offers from employers in Ontario’s Atlantic region (Ontario is primarily served by other regional programs, but many come to Ontario after settling in the Atlantic region).
d. Temporary Foreign Worker Program (TFWP) and International Mobility Program (IMP)
- These allow foreign nationals to come to Ontario temporarily for work and possibly transition to permanent status.
3. Provincial Nominee Program (OINP) vs. Express Entry
Ontario often aligns with Express Entry for skilled workers. If you’re eligible for one of the Express Entry-managed programs, you can receive an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residence. Provincial nominees from Ontario, once nominated by the OINP, get an additional 600 points in the Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS), which increases their chances of receiving an invitation to apply for permanent residency.
4. Student Immigration
Ontario is home to some of Canada’s top universities and colleges, making it a popular destination for international students. After completing their studies, students may apply for the Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP), which allows them to gain Canadian work experience and eventually transition to permanent residency. Ontario has several pathways for international students to apply for permanent residence, such as through the Ontario Immigrant Nominee Program or the Express Entry system.
5. Temporary Work Permits
Foreign workers who are temporarily employed in Ontario can apply for work permits through the Temporary Foreign Worker Program (TFWP) or the International Mobility Program (IMP). These programs allow you to live and work in Ontario for a limited period and potentially transition to permanent residence if eligible.
6. Refugee and Asylum Status
Ontario is also a key destination for refugees. Individuals seeking asylum in Canada can apply for refugee status, and Ontario provides services for settlement and integration.
7. Living in Ontario
- Cost of Living: Ontario’s cost of living varies by city, with Toronto being one of the most expensive cities in Canada. Other cities like Ottawa, Kitchener-Waterloo, and Hamilton offer more affordable living options.
- Healthcare: Ontario provides healthcare services through the Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP) for residents.
- Education: Ontario is home to world-renowned universities and colleges, offering opportunities for international students and those pursuing further education.
8. Key Requirements for Immigration to Ontario
- Language Proficiency: Many immigration streams require proficiency in English or French, usually demonstrated by language tests like IELTS or TEF.
- Education: Having an educational credential (often equivalent to a Canadian high school diploma or higher) is important for most skilled worker streams.
- Work Experience: Most skilled worker and trade programs require specific years of work experience in certain occupations.
- Job Offer: For many immigration pathways, having a valid job offer from an Ontario employer is necessary.
If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
SAY YES (OUI) TO QUEBEC


Quebec is the largest Canadian Province by geographical landmass. With a population of about 9 million, (about 14% of the entire Canadian Population) Quebec is the second most populous Province in Canada.
Quebec’s official language is French and the only Francophone-majority Province in Canada. Quebec is world-known for its mining, paper mills, hockey, art, culture, literature, TV shows, and festivals.
The name Quebec derives from the aboriginal language of Algonquin, which means “Narrow Passage” or “Strait.”
Here are a few key details about it:
1. Geography
- Location: Quebec is the largest province in Canada by area, covering over 1.5 million square kilometers (about 600,000 square miles). It borders the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, and several other provinces such as Ontario and Newfoundland and Labrador.
- Cities: Quebec’s largest city is Montreal, followed by the capital, Quebec City. Montreal is a major cultural and economic hub, while Quebec City is known for its well-preserved Old Town, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- Natural Beauty: The province features a wide range of landscapes, from the boreal forests and tundra of the north to the rolling hills and rivers of the south. Popular outdoor activities include skiing, hiking, and wildlife watching.
2. Language and Culture
- French: Quebec is the only province in Canada where French is the official language, and the majority of the population speaks French as their first language. This makes it unique in North America, where English dominates.
- Cultural Identity: Quebec has a strong sense of identity, with its own traditions, cuisine, and festivals. For example, the province is famous for its food, like poutine (fries with cheese curds and gravy), tourtière (meat pie), and maple syrup.
- Art and Music: Quebec has a vibrant cultural scene with a thriving music, theater, and film industry. The Montreal International Jazz Festival and the Quebec City Winter Carnival are just a couple of the major events that draw tourists from around the world.
3. History and Politics
- French and British Heritage: Quebec’s history is deeply influenced by both French and British colonization. Initially a French colony, it was ceded to Britain in 1763 after the Seven Years’ War. This event set the stage for the province’s distinct bilingual nature.
- Separatism Movement: Quebec has a history of separatist sentiment, with several referendums in the 1980s and 1990s on the question of whether the province should become an independent nation. While both referendums were defeated, the question of Quebec’s political status remains an important issue in its politics.
- Quebecois Nationalism: Many people in Quebec identify strongly as “Quebecois” rather than Canadian, and there are political parties that advocate for the promotion of the French language and Quebec’s autonomy.
4. Economy
- Natural Resources: Quebec is rich in natural resources, including hydroelectric power (it’s a major producer of hydroelectricity), forestry, and mining. The province is a leader in renewable energy production.
- Technology and Aerospace: Montreal, in particular, has become a hub for high-tech industries, including artificial intelligence, video game development, and aerospace manufacturing.
- Agriculture: Quebec also has a significant agricultural industry, known especially for its dairy products, maple syrup production, and grains.
5. Education and Research
- Quebec is home to some of Canada’s top universities, including McGill University and Université de Montréal in Montreal, and Laval University in Quebec City. The province places a strong emphasis on research and development, particularly in fields like technology, health sciences, and environmental studies.
6. Legal System
- Quebec has a unique legal system in Canada, based on civil law, influenced by the Napoleonic Code, rather than the common law system used in the rest of Canada and the United States.
MONTREAL




Montreal is Quebec’s largest city. With a population of about 2 million inhabitants, Montreal is also the second largest in Canada and the ninth in North America.
Montreal is a vibrant and culturally rich city that is known for its unique blend of French and English influences. Here are some key highlights about Montreal:
1. Cultural Diversity
- Montreal has a large immigrant population, with people from all over the world contributing to the city’s multicultural atmosphere. While French is the official language, you’ll hear English, Spanish, Arabic, and many other languages spoken throughout the city.
2. Language
- French is the predominant language in Montreal, and it has a distinct local accent. However, English is widely spoken, particularly in the downtown core, and many residents are bilingual. The city often feels like a blend of both French and North American cultures.
3. Arts and Festivals
Montreal is famous for its art scene and festivals. Some of the most popular ones include:
- Montreal International Jazz Festival: One of the largest jazz festivals in the world.
- Just for Laughs: The world’s largest comedy festival.
- Montreal World Film Festival: Celebrates cinema from around the world.
- Montreal en Lumière: A winter festival celebrating food, culture, and light.
The city also has a thriving theater, dance, and visual arts scene, with iconic institutions like the Montreal Museum of Fine Arts and the Place des Arts.
4. Food Scene
Montreal’s food culture is a mix of French, Québécois, and international influences. Some must-try foods include:
- Poutine: A Quebecois dish of fries, cheese curds, and gravy.
- Montreal-Style Bagels: Smaller, denser, and sweeter than New York-style bagels.
- Smoked Meat Sandwich: A Montreal classic, usually served with mustard on rye bread.
The city is also home to an incredible variety of restaurants, from high-end dining to casual eateries.
5. Old Montreal (Vieux-Montréal)
- The historic district of Old Montreal is a popular area for tourists and locals alike. The cobblestone streets, 17th-century buildings, and landmarks such as the Notre-Dame Basilica, Old Port, and Place Jacques-Cartier make it one of the most charming parts of the city.
6. Mount Royal (Mont Royal)
- Mount Royal is the park at the heart of the city, offering beautiful views of the skyline. It’s a great spot for hiking, picnicking, and outdoor activities, especially in the warmer months. In the winter, it turns into a popular location for sledding, ice skating, and cross-country skiing.
7. Sports
Montreal has a passionate sports culture, with several major teams:
- Montreal Canadiens: One of the most successful and beloved hockey teams in the NHL.
- CF Montreal: The city’s professional soccer team.
- The city also has a love for baseball (with the now-defunct Expos) and basketball, with growing support for the NBA’s Toronto Raptors.
8. Weather
- Montreal has a cold, snowy winter with temperatures often dropping well below freezing. Winters can be challenging, but they come with their own charm and outdoor activities. Summers, however, are warm and pleasant, making it a great time to explore the city’s parks and outdoor festivals.
9. Transportation
Montreal has an extensive public transportation system, including buses and the Montreal Metro, which is one of the most efficient subway systems in North America. The city is also very bike-friendly, with an impressive network of bike paths.
10. Education
Montreal is home to several world-class universities, including McGill University (which has a strong international reputation), Université de Montréal, and Concordia University.
QUEBEC IMMIGRATION
Immigrating to Quebec involves a unique process compared to other provinces in Canada, as Quebec has more autonomy over its immigration policies. Here are the key pathways and requirements for immigrating to Quebec:
1. Quebec Skilled Worker Program (QSWP)
This is the primary immigration stream for skilled workers who wish to settle in Quebec. It’s based on a points system that considers factors like education, work experience, age, language proficiency, and adaptability.
Key Requirements:
- Work Experience: You need to have relevant work experience in a skilled occupation.
- Education: The level of education you have affects your points score.
- Language Proficiency: French is a significant factor. While English may be accepted in some cases, a strong knowledge of French is highly advantageous, as Quebec is a French-speaking province.
- Age: Younger applicants tend to score better
- Job Offer: Not mandatory but can add points to your application.
2. Quebec Experience Program (PEQ)
The PEQ is for those who have already lived and worked or studied in Quebec. It’s designed to fast-track permanent residency for individuals with experience in the province.
Key Requirements:
- Work Experience: You need to have at least 12 months of full-time work experience in Quebec in a skilled job (NOC 0, A, or B).
- Study: Alternatively, if you’ve studied at a recognized educational institution in Quebec for at least 1,800 hours (or 1 year), you may be eligible.
- Language Proficiency: You must demonstrate intermediate proficiency in French (usually through a test such as TEF or TCF).
3. Quebec Business Immigration
Quebec offers various business immigration streams, such as the Entrepreneur Program, Investor Program, and Self-employed Program, for those who want to start or invest in a business in the province.
Key Requirements:
- Entrepreneur Program: Applicants must prove that they have the resources and experience to establish or acquire a business in Quebec.
- Investor Program: Typically requires significant financial investment (usually around CAD 1.2 million).
- Self-employed Program: Designed for individuals who plan to work as self-employed in Quebec, such as artists or professionals.
4. Family Sponsorship
If you have a close family member who is a Canadian citizen or permanent resident living in Quebec, they may be able to sponsor your immigration.
Key Requirements:
- Relationship: You must be a spouse, dependent child, parent, or other qualifying relative.
- Sponsor’s Eligibility: Your sponsor must meet certain income requirements and prove that they can support you financially.
5. Quebec Immigration Selection Certificate (CSQ)
Before applying to the federal government for permanent residency, you must first obtain a Quebec Selection Certificate (Certificat de Sélection du Québec, or CSQ). To get the CSQ, you need to be approved by the Quebec immigration authorities based on one of the programs mentioned above.
Once you have a CSQ, you can apply to the federal government for permanent residency.
6. Temporary Residency Pathways
In addition to permanent residency programs, Quebec also has pathways for temporary residents, such as those coming for work, study, or as visitors. After working or studying in Quebec temporarily, some individuals may transition to permanent residency via the PEQ or other programs.
Important Notes:
- Language: Quebec’s immigration system is heavily influenced by the province’s commitment to the French language. Therefore, proficiency in French (or English, depending on the program) is often a key factor.
- Processing Times: The processing times for Quebec immigration can vary depending on the program. It may take several months to a few years, so it’s essential to prepare your documents ahead of time.
- Legal Assistance: Many applicants choose to work with a licensed immigration consultant or lawyer, especially for more complex cases like business immigration or family sponsorships.
If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
BRITISH COLUMBIA




British Columbia is indeed the precious jewel of the Pacific. With a diverse geography of rolling grasslands to rugged landscapes, rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, dense forests, beautiful blue lakes, sky-scrapping mountains, and inland deserts, indeed B.C. is the most diversely beautiful Province in Canada.
British Columbia’s economy runs on creativity, tourism, mining, and maritime trade. Here are some more key facts about British Columbia:
Geography:
- Diverse Landscape: BC is known for its stunning natural beauty, including rugged coastlines, snow-capped mountains, temperate rainforests, and vast wilderness. The province has a variety of ecosystems, from alpine areas to coastal wetlands.
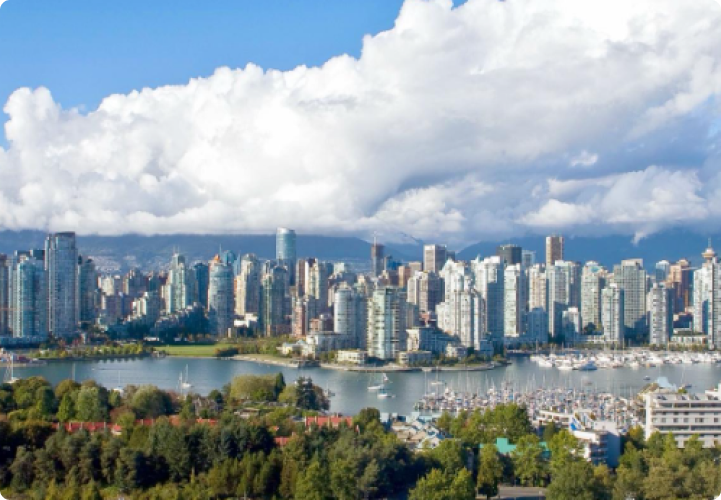
- Vancouver: The largest city in BC, Vancouver is a major urban center known for its multicultural population, film industry, and proximity to both mountains and the ocean. It’s often ranked as one of the most livable cities in the world.
- Victoria: The capital city of BC, located on Vancouver Island, is known for its historical architecture, British colonial heritage, and mild climate.
Climate:
- Coastal Climate: The coastal regions of BC, such as Vancouver, have a temperate maritime climate, with mild, wet winters and cool, dry summers. This is due to the moderating effect of the Pacific Ocean.
- Interior Climate: In the interior, the climate can be more continental, with colder winters and hotter, drier summers. This is particularly true for areas like the Okanagan Valley, which is known for its vineyards and agricultural production.
- Mountain Climate: The mountainous regions of BC can have colder temperatures and heavy snowfall in winter, making them popular for skiing and other winter sports.
Economy:
- Natural Resources: BC’s economy has historically been based on natural resources, including forestry, mining, and fisheries. The province is one of Canada’s largest producers of timber.
- Technology & Innovation: Vancouver and Victoria are growing tech hubs, with a strong presence in software development, digital media, and biotechnology.
- Tourism: BC is a major tourism destination, attracting visitors for outdoor activities like hiking, skiing, and wildlife viewing. The province’s national parks and scenic drives (such as the Sea-to-Sky Highway) are popular attractions.
- Film Industry: Vancouver is often called “Hollywood North” due to its large film and television production industry, including many productions that choose BC for its diverse settings and tax incentives.
Indigenous Peoples:
- British Columbia is home to a large number of Indigenous communities, each with its own unique cultures, languages, and traditions. The province is recognized for having one of the most diverse Indigenous populations in Canada.
- There are many land rights issues and reconciliation efforts, including modern treaties, land claims, and self-governance agreements. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission’s work is a significant part of BC’s ongoing efforts to address the impacts of colonialism on Indigenous peoples.
Culture:
- Outdoor Lifestyle: BC residents enjoy an active outdoor lifestyle, including hiking, skiing, cycling, kayaking, and more. This connection to nature is a strong part of the province’s identity.
- Multiculturalism: BC is one of Canada’s most multicultural provinces, with significant immigrant populations, particularly from Asia. This cultural diversity is reflected in the province’s food, festivals, and arts scene.
- Arts & Entertainment: BC has a vibrant arts and entertainment community, with a strong presence in theater, music, dance, and visual arts. Vancouver is known for its film and TV industry, and the province also has several film festivals, including the Vancouver International Film Festival (VIFF).
Transportation:
- Public Transit: Major cities like Vancouver have well-developed public transit systems, including buses, SkyTrain, and ferries. The TransLink system serves Greater Vancouver, while BC Ferries operates routes between the mainland and Vancouver Island, as well as other coastal communities.
- Road Networks: BC has a network of highways connecting cities and remote communities, including the scenic Sea-to-Sky Highway and the Trans-Canada Highway.
- Air Travel: Vancouver International Airport (YVR) is one of Canada’s busiest airports, offering both domestic and international flights.
Notable Landmarks & Attractions:
- Whistler: A world-renowned ski resort located just north of Vancouver, famous for its skiing, snowboarding, and year-round outdoor activities.
- Stanley Park: A large urban park in downtown Vancouver, offering walking trails, beaches, and the Vancouver Aquarium.
- Butchart Gardens: A historic garden near Victoria, offering stunning floral displays and scenic walking paths.
- Okanagan Valley: Known for its wine production, fruit orchards, and hot, dry summers, this region is a popular spot for wine tourism.
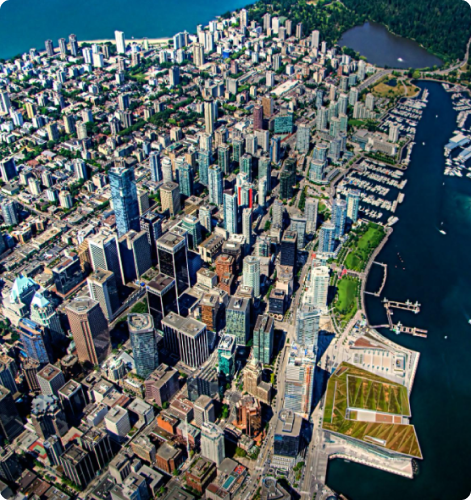
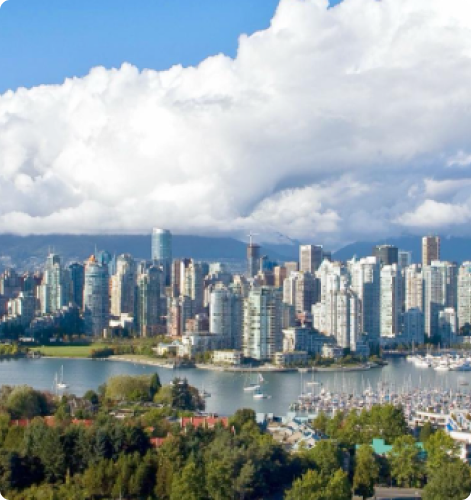
VANCOUVER
Vancouver is British Colombia’s biggest and most populated city. About 700,000 people of all colors and creeds call Vancouver home. The Greater Metropolitan Vancouver has over 3 million inhabitants.
Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada. It is also the fourth highest in North America after New York, San Francisco, and Mexico City.
Vancouver has been a very attractive place for immigrants for ions. The flow of Indigenous immigration to Vancouver began more than 10,000 years ago.
Vancouver’s immense beauty has turned it into a popular tourist destination. Vancouver is also known as the Hollywood of the North.
All in all, Vancouver is a vibrant city that is world-known for its stunning natural beauty, as it’s surrounded by mountains, forests, and the Pacific Ocean. Here are a few key points about Vancouver:
1. Natural Beauty and Outdoor Activities
- Vancouver is famous for its access to a wide variety of outdoor activities, including hiking, skiing, biking, kayaking, and more. Stanley Park, one of the largest urban parks in North America, is located right in the city and offers scenic views, trails, and beaches.
- The nearby Whistler resort is renowned for skiing and snowboarding in the winter and hiking and mountain biking in the summer.
2. Cultural Diversity
- Vancouver is one of Canada’s most diverse cities, with a large immigrant population. The city’s cultural diversity is reflected in its cuisine, festivals, and neighborhoods.
- Areas like Richmond, Surrey, and Kitsilano are known for their multicultural communities and a wide range of international restaurants and markets.
3. Economy and Industry
- Vancouver has a strong economy driven by industries such as film and television production, technology, tourism, and natural resources.
- The city is often called “Hollywood North” because it is a major hub for film and TV production, with many major productions filmed here due to its diverse landscapes and tax incentives.
4. Climate
- Vancouver has a temperate climate, with mild, rainy winters and cool, dry summers. It’s known for its wet winters, especially in the form of rain, though snow is rare in the city center (though the nearby mountains get plenty of snow).
- The city is often one of the warmest places in Canada during the winter months.
5. Transportation
- Vancouver has an excellent public transportation system, including buses, a SkyTrain (a light rail system), and ferries to nearby areas like Vancouver Island.
- Biking is also popular, and the city is known for its bike-friendly infrastructure
6. Education and Research
- The city is home to major educational institutions like the University of British Columbia (UBC) and Simon Fraser University (SFU), both of which are known for their research programs and vibrant student communities.
7. Real Estate
- Vancouver has one of the most expensive real estate markets in the world, with high demand for housing driving up prices, especially in neighborhoods like Downtown, West End, and Yaletown.



IMMIGRATION TO BRITISH COLUMBIA
Immigrating to British Columbia (BC) is an exhilarating option on so many levels due to its strong economy, diverse culture, and beautiful landscapes. There are various pathways through which individuals can immigrate to BC, whether as workers, entrepreneurs, students, or family members of Canadian citizens or permanent residents. Here are the key pathways for immigration to British Columbia:
1. Express Entry BC (EEBC)
The Express Entry BC program is aligned with the federal Express Entry system, which manages applications for permanent residence under the following federal economic immigration programs:
- Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSW)
- Federal Skilled Trades Program (FST)
- Canadian Experience Class (CEC)
If you’re eligible for one of these federal programs, you can apply to the BC Provincial Nominee Program (BC PNP) Express Entry BC stream, which gives you a nomination for permanent residency and can help speed up the immigration process.
Eligibility requirements include:
- A valid Express Entry profile.
- A job offer in BC in a high-demand occupation (depending on the stream).
- Meeting minimum work experience and language requirements.
2. Skills Immigration (SI)
The Skills Immigration stream is designed for workers who have skills that are in demand in BC. There are multiple sub-categories under this stream:
- Skilled Worker: For individuals with a job offer in a skilled occupation (NOC 0, A, or B).
- International Graduate: For international students who have graduated from a recognized BC post-secondary institution.
- International Post-Graduate: For individuals who have completed a graduate degree (Master’s or Ph.D.) in natural, applied, or health sciences from a BC institution.
- Entry-Level and Semi-Skilled Worker: For workers in specific entry-level or semi-skilled occupations, usually in industries such as tourism, hospitality, or agriculture.
To be eligible, applicants typically need a full-time, permanent job offer from a BC employer.
3. BC Provincial Nominee Program (BC PNP)
The BC Provincial Nominee Program (BC PNP) is a pathway for skilled workers, entrepreneurs, and graduates to live and work in BC. There are several streams under the BC PNP:
- Express Entry BC (as mentioned above).
- Skills Immigration (also mentioned above).
- Entrepreneur Immigration: For individuals who want to start or invest in a business in BC.
- Tech Pilot: For individuals with a job offer in BC’s technology sector.
4. Entrepreneur Immigration
The Entrepreneur Immigration stream is designed for individuals who want to establish, invest in, or purchase a business in BC. This stream has several sub-categories:
- Entrepreneur Immigration: For experienced entrepreneurs who wish to start a business in BC.
- International Graduate Entrepreneur: For international students who have recently graduated from a BC post-secondary institution and want to start a business.
- Regional Entrepreneur: For entrepreneurs who wish to establish a business in smaller communities outside of Vancouver and Victoria.
5. Family Sponsorship
- Spouses or common-law partners
- Dependent children
- Parents and grandparents (through the Parent and Grandparent Program, if available)
Sponsorships are typically handled through the federal government, but applicants must demonstrate their relationship with the sponsor and meet other specific requirements.
6. Student Immigration
BC has many prestigious post-secondary institutions, and international students can apply for a study permit to attend these institutions. After graduation, international students may be eligible for the Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP), which allows them to work in BC for a period of time (typically up to 3 years). This work experience can then lead to permanent residency through programs like Express Entry or the Skills Immigration stream.
7. Temporary Worker Program
This program is for individuals who want to work temporarily in BC. The Temporary Foreign Worker Program (TFWP) and International Mobility Program (IMP) allow employers to hire foreign workers for jobs that cannot be filled by Canadian citizens or permanent residents. Some temporary workers may later transition to permanent residency through the BC PNP or other pathways.
8. Atlantic Immigration Program
Though this program is focused on the Atlantic provinces, there are provisions for individuals who may want to move to BC as a secondary destination. BC participates in various inter-provincial agreements, which can allow individuals to transfer their immigration status to BC under specific conditions.
Key Considerations
- Language Proficiency: Most immigration streams in BC require applicants to demonstrate proficiency in either English or French through language tests like IELTS or TEF.
- Work Experience: Many immigration programs require work experience in a skilled occupation, typically at least one year in the last ten years.
- Job Offer: Many of the streams, including Skills Immigration and Express Entry BC, require a full-time, permanent job offer from a BC employer.
- BC PNP Points: The BC PNP uses a points-based system that evaluates factors like age, education, work experience, and language skills to rank candidates. Higher points increase the chances of getting an invitation to apply.
Immigrating to British Columbia offers numerous opportunities across various streams and pathways, whether you are a skilled worker, entrepreneur, student, or family member. The process can be competitive, so it’s crucial to understand the eligibility requirements and ensure you have the necessary qualifications and documents. Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers are ready, willing, and able to help you turn your immigration dreams into realities. And the journey of a thousand miles starts with a Call or Click.
ALBERTA
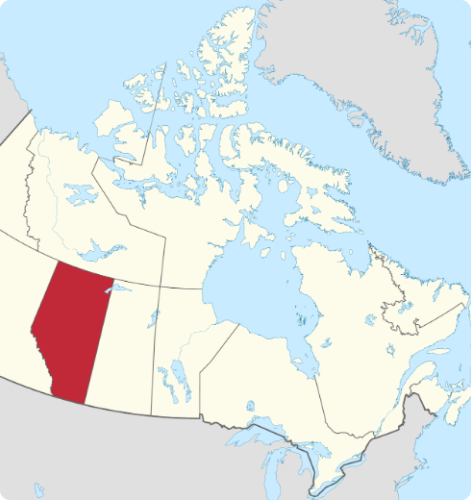




Alberta is the fourth-largest Province in terms of geography and population in Canada. The eastern Great Plains and the western Rocky Mountains make Alberta a magnificently diverse and beautiful landscape. Alberta is home to about 4.5 million inhabitants. Its capital city is Edmonton, while Calgary is Alberta’s largest city. If you are into livestock, agriculture, oil, and gas industries, Alberta is yours to explore.
Here are some key facts about Alberta:
1. Geography and Nature:
- Rocky Mountains: Alberta is home to part of the Canadian Rockies, with iconic peaks such as Mount Columbia and Mount Assiniboine. Banff National Park and Jasper National Park are major tourist attractions within the Rockies.
- Prairies: The southern and central parts of the province consist of vast, flat prairies, which are ideal for agriculture, particularly wheat and canola farming.
- Lakes and Rivers: Alberta has numerous lakes and rivers, including the large Lake Athabasca and the Bow River, famous for its beautiful setting and recreation opportunities.
2. Capital and Major Cities:
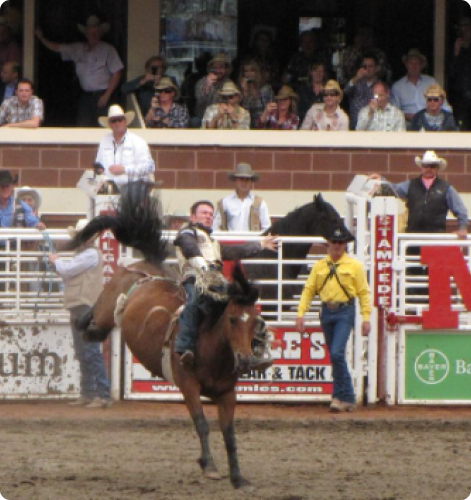
- Edmonton is the capital city of Alberta and serves as a major cultural, political, and economic hub. It’s also known for its large shopping malls, such as the West Edmonton Mall, one of the largest in North America.
- Calgary is Alberta’s largest city and an important financial and industrial center. It is especially well known for the Calgary Stampede, a huge rodeo and exhibition event held every summer.
3. Economy:
- Alberta has a resource-rich economy. It is one of the world’s largest oil producers, especially from the oil sands of the Athabasca region. The oil and gas industry is a cornerstone of Alberta’s economy.
- The province is also known for its agricultural production, particularly cattle ranching, wheat, barley, and other grains.
- There is a growing focus on renewable energy, technology, and innovation as Alberta diversifies its economy.
4. Culture and Lifestyle:
- Alberta has a strong outdoor culture, with activities such as hiking, skiing, snowboarding, fishing, and mountain biking being popular year-round.
- The Calgary Stampede is a major cultural event, drawing visitors from around the world for its rodeo, music, and parade.
- Albertans are known for their friendly, welcoming attitude, with many people moving to the province for its booming job market.
5. Climate:
- Alberta experiences a wide variety of climates due to its diverse geography. The southern part of the province has a more temperate climate with hot summers and cold winters, while the northern parts have a more continental climate, experiencing colder winters and shorter summers.
- The mountains create a phenomenon known as the “Chinook winds,” which can cause rapid warming, especially in Calgary.
6. Wildlife and Conservation:
- Alberta has an impressive array of wildlife, including grizzly bears, black bears, moose, elk, bison, and wolves, especially in its national parks and protected areas.
- The province places a strong emphasis on conservation, with many areas set aside for wildlife protection and outdoor recreation.
EDMONTON
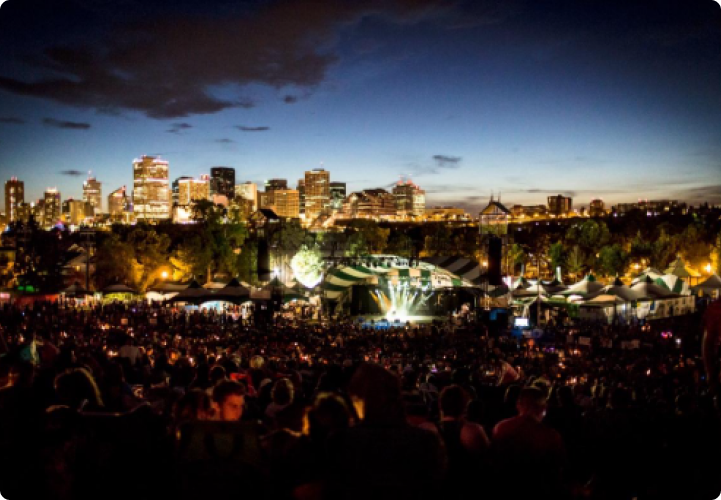


Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River. Edmonton is the capital city of Alberta. Located in the central part of the province, it is the fifth-largest city in Canada by population. Known as the “Gateway to the North,” Edmonton serves as a major hub for oil and gas, as well as being a cultural, political, and economic center of northern Alberta.
Here are a few key features and highlights of Edmonton:
1. Climate: Edmonton has a cold climate, with long, harsh winters and short, warm summers. Winters often bring heavy snow and temperatures can drop well below freezing, while summers can see temperatures reaching into the high 20s and low 30s Celsius.
2. Edmonton Oilers: The city is home to the Edmonton Oilers, an NHL team with a rich history and a passionate fan base. The Oilers are known for their iconic players like Wayne Gretzky, who played for the team in the 1980s and helped lead them to multiple Stanley Cup championships.
3. Cultural Scene: Edmonton boasts a vibrant arts and cultural scene. The Edmonton International Fringe Festival is one of the largest fringe festivals in the world. The city is also home to numerous theaters, art galleries, and music festivals.
4. West Edmonton Mall:
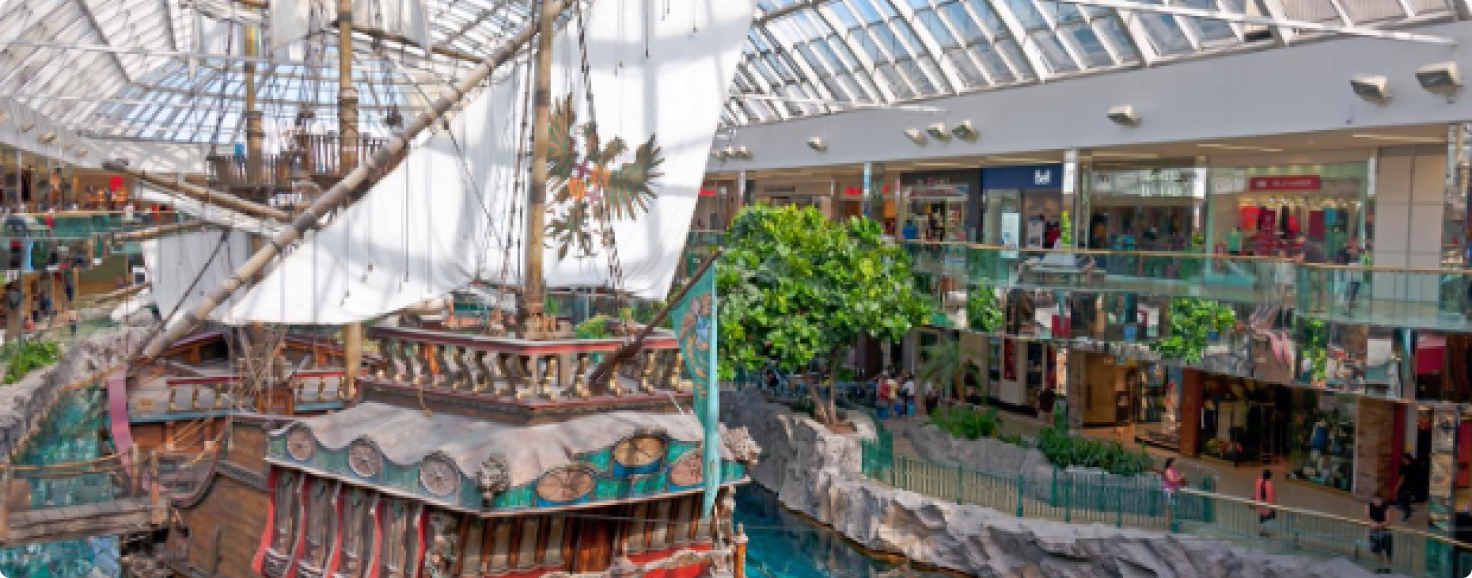

One of the largest shopping malls in North America, West Edmonton Mall offers a wide range of shopping, dining, and entertainment options. It includes attractions like an indoor water park, ice rink, and amusement park.
5. River Valley: Edmonton is known for its extensive river valley, which stretches along the North Saskatchewan River. The city’s river valley parks offer trails for hiking, biking, and cross-country skiing in the winter.
6. Education : Edmonton is home to several post-secondary institutions, including the University of Alberta, one of Canada’s top research universities.
7. Energy Industry: The city’s economy is closely tied to the oil and gas sector, and it’s often referred to as the “Energy Capital of Canada.” The city also serves as a hub for the Canadian oil sands industry, which is concentrated to the north of the city.
IMMIGRATION TO ALBERTA
Immigrating to Alberta offers a range of opportunities due to the province’s strong economy, high quality of life, and diverse communities. Alberta is one of the best provinces in Canada for immigrants, with a growing demand for skilled workers in various industries, including energy, agriculture, technology, healthcare, and construction. Below is an overview of the pathways for immigration to Alberta:
1. Alberta Immigrant Nominee Program (AINP)
The Alberta Immigrant Nominee Program (AINP) allows the provincial government to nominate individuals for permanent residence in Canada. There are several streams under the AINP:
- Alberta Opportunity Stream (AOS): For workers with a job offer from an Alberta employer in a skilled occupation. The applicant must meet certain criteria such as work experience, language proficiency, and education.
- Alberta Express Entry Stream: For candidates who are already in the federal Express Entry pool. The province selects individuals based on their skills and experience to meet the province’s labor market needs.
- Alberta Self-Employed Farmer Stream: For individuals who wish to start a farming business in Alberta and meet the investment and experience requirements in agriculture.
- Alberta International Graduate Entrepreneur Stream: For individuals who have recently graduated from an Alberta post-secondary institution and want to start or buy a business in the province.
2. Federal Express Entry System
The Express Entry System is Canada’s main way of managing permanent residency applications. Alberta frequently selects candidates from the Express Entry pool who have the skills and experience needed in the province. Under this system, there are three programs you can apply through:
- Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP): For individuals with work experience in skilled occupations (usually requiring a post-secondary degree).
- Federal Skilled Trades Program (FSTP): For individuals with work experience in a skilled trade (e.g., electrician, plumber).
- Canadian Experience Class (CEC): For individuals who already have Canadian work experience, typically gained through a temporary work visa.
3. Alberta Provincial Nominee Program (PNP) via Express Entry
Individuals who are already in the Express Entry pool and have received a nomination from Alberta under the Alberta Express Entry Stream can receive additional points toward their Express Entry Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) score. A nomination from Alberta is a significant boost to your chances of receiving an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residency.
4. Work Permits and Temporary Residence
Before applying for permanent residency, some immigrants come to Alberta on a temporary work permit. Common pathways to gain a work permit include:
- Labor Market Impact Assessment (LMIA): A process through which employers in Alberta can hire foreign workers if they can prove that no Canadians or permanent residents are available to do the job.
- Open Work Permits: These permits allow workers to take any job with any employer in Alberta. Spouses or common-law partners of temporary foreign workers can also apply for open work permits.
5. Business Immigration
If you are a businessperson or investor, there are specific programs to help you immigrate:
- Alberta Immigration Entrepreneur Stream: For individuals who want to invest in or start a business in Alberta. This stream requires a minimum net worth and investment and may involve operating the business for a period before applying for permanent residence.
- Self-Employed Farmer Stream: For individuals who intend to establish a farming business in Alberta. This stream has specific investment and business experience requirements.
6. Family Sponsorship
If you have family members who are Canadian citizens or permanent residents in Alberta, they may be able to sponsor you to come to the province. Family sponsorship allows Canadian citizens or permanent residents to sponsor close relatives, including spouses, parents, children, and other dependents, for permanent residency.
7. Alberta’s Economy and Job Market
Alberta is a prosperous province with a strong economy primarily based on the oil and gas industry. However, other sectors such as agriculture, technology, healthcare, and manufacturing also offer a variety of career opportunities for immigrants.
- Oil and Gas: Alberta’s energy sector remains one of the largest industries, offering jobs for skilled workers such as engineers, technicians, and tradespeople.
- Technology: Alberta’s tech sector is expanding, with growth in areas like software development, IT support, and cybersecurity.
- Healthcare: Alberta has a significant demand for healthcare workers, including nurses, physicians, and allied health professionals.
- Agriculture: Agriculture continues to be a major contributor to Alberta’s economy, requiring farmers, agricultural technicians, and workers in related fields.
- Agriculture: Agriculture continues to be a major contributor to Alberta’s economy, requiring farmers, agricultural technicians, and workers in related fields.
8. Requirements for Immigration to Alberta
- Language Proficiency: Depending on the immigration stream, you will need to provide proof of language proficiency in English or French, typically through recognized language tests such as IELTS or TEF.
- Educational Credentials: A degree or diploma may be required depending on the job you’re applying for or the immigration program you are applying under. In some cases, foreign credentials must be assessed by an authorized body to ensure they are equivalent to Canadian standards.
- Work Experience: Relevant work experience is typically required for most skilled immigration streams. This can be in fields like engineering, healthcare, IT, and business management.
9. Cost and Processing Time
- The processing time and costs associated with immigration applications vary based on the program. For example, the Express Entry process is generally faster, but the Alberta Immigrant Nominee Program (AINP) may take several months depending on the stream and the number of applicants.
10. Settlement and Support Services
Alberta provides a variety of settlement services for immigrants, including help with finding housing, accessing healthcare, learning English or French, and finding employment. The provincial government, as well as local community organizations, offer these services to help newcomers adjust to life in Alberta.
If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
MANITOBA


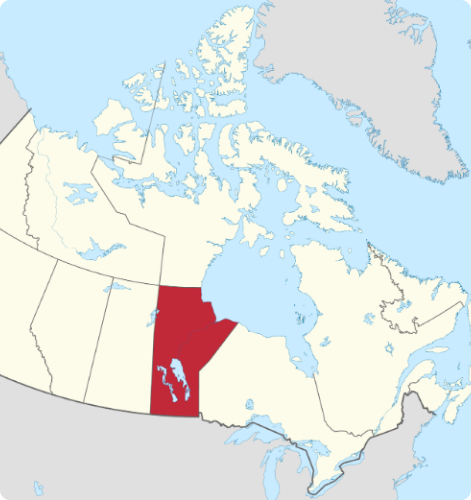
With a population of about 1.5 million people, Manitoba is Canada’s fifth-largest Province.
The name Manitoba derives from the aboriginal languages, which refers to this beautiful landscape “Manitouwapow” or “Manidoobaa.”
Manitoba is known for its diverse geography, which includes vast prairies, boreal forests, and numerous lakes, including Lake Winnipeg, one of the largest freshwater lakes in the world.
Here are some key points about Manitoba:
1. Geography
- Landscape: Manitoba has a diverse landscape ranging from flat prairies to northern boreal forests. The southern part of the province is part of the Great Plains, while the northern part has rugged terrain and numerous lakes.
- Lakes and Rivers: The province is home to many lakes, such as Lake Manitoba, Lake Winnipeg, and Lake of the Woods. The Red River, which runs through Winnipeg, is another notable geographical feature.
2. Climate
- Manitoba experiences a continental climate, with cold winters and warm summers. Winters can be very harsh, with temperatures frequently dipping below freezing, while summers are typically warm, with occasional thunderstorms.
- The province is known for its extreme weather, including heavy snowfalls and thunderstorms.
3. History
- Manitoba became a province in 1870, making it the fifth province to join Canada. It was originally a part of the Red River Settlement, which was established by Métis and French-speaking settlers.
- The Métis people, a group of mixed Indigenous and European descent, played a significant role in the province’s history, particularly in the resistance to Canadian expansion in the 19th century.
4. Economy
- The economy of Manitoba is diverse, with major industries including agriculture, manufacturing, natural resources, and services. The province is known for its agricultural output, particularly wheat, canola, and livestock.
- Manitoba also has a significant mining industry, with mineral resources such as nickel, copper, and zinc. In recent years, there has also been growth in the technology sector, particularly in Winnipeg.
5. Culture
- Manitoba is culturally rich and diverse, with a significant Indigenous population, as well as many communities of European descent, particularly of Ukrainian, German, and Scandinavian origins.
- The province is known for its arts scene, including the Winnipeg Symphony Orchestra, the Royal Winnipeg Ballet, and many festivals such as the Winnipeg Folk Festival and Folklorama.
6. Tourism and Nature
- Manitoba offers outdoor activities such as hiking, fishing, canoeing, and snowmobiling. It is home to several national parks, including Riding Mountain National Park and Wapusk National Park, which is known for its polar bear population.
- The northern region of the province is known for its wilderness and is a popular destination for wildlife enthusiasts, especially those looking to see polar bears and beluga whales.
7. Notable Attractions
- The Forks (Winnipeg): A popular historic site and market, where the Red and Assiniboine Rivers meet.
- Royal Canadian Mint (Winnipeg): The facility where Canadian coins, as well as coins for other countries, are produced.
- Churchill: Known as the “Polar Bear Capital of the World,” Churchill is a remote northern town famous for its polar bear sightings, beluga whale watching, and northern lights.
8. Education
- Manitoba is home to several universities and colleges, with the University of Manitoba being the largest and oldest in the province.
- The province places a strong emphasis on education and research, particularly in fields such as agriculture, the environment, and Indigenous studies.
9. Language
- English is the dominant language spoken in Manitoba, but there are also significant French-speaking communities, particularly in the southeast. Indigenous languages such as Cree and Ojibwe are spoken by many First Nations communities.
10. Indigenous Peoples
- Manitoba has a large Indigenous population, including First Nations, Métis, and Inuit peoples. Indigenous culture and traditions are an integral part of the province’s identity and history.
- The Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada, which aimed to address the legacy of residential schools, had a strong connection to Manitoba, where many residential schools were located.
Manitoba is often seen as a blend of urban and rural environments, offering a mix of natural beauty, cultural richness, and a high quality of life.
If you are considering immigrating to Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
WINNIPEG
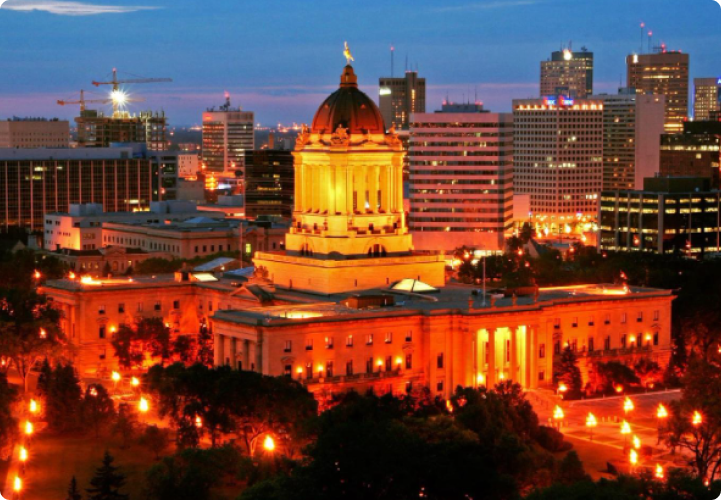




Winnipeg is the largest city and capital of Manitoba. It has a population of about 850,000 people, which makes it the sixth-largest Canadian city.
The name Winnipeg is a derivative of native languages, which means “Muddy Water.” Known for its rich cultural history, Winnipeg lies at the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine Rivers. The city is often referred to as the “Gateway to the West” because of its historical importance as a transportation hub for settlers heading westward in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Some key features of Winnipeg include:
1. Climate: Winnipeg is famous for its extreme temperatures. Winters can be harsh, with temperatures often dropping below -20°C (-4°F) in January, while summers can be hot, with temperatures reaching over 30°C (86°F) in July. It’s one of Canada’s coldest major cities in the winter, but residents embrace it with a variety of winter sports and activities.
2. Cultural Scene: Winnipeg is home to many arts and cultural institutions, including the Royal Winnipeg Ballet, the Winnipeg Symphony Orchestra, and the Manitoba Museum. The city also hosts the annual Winnipeg Folk Festival, one of the largest folk music festivals in the country.
3. Historical Significance: Winnipeg played an important role during Canada’s westward expansion, particularly with the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway. The city’s Exchange District is a National Historic Site, with many well-preserved early 20th-century buildings.
4. Notable Attractions:
- The Forks: A popular gathering place where the Red and Assiniboine Rivers meet, offering markets, restaurants, museums, and recreational activities.
- The Canadian Museum for Human Rights: This stunning architectural landmark tells the story of human rights in Canada and around the world.
- Assiniboine Park: A large urban park that includes the Assiniboine Park Zoo, beautiful gardens, walking paths, and outdoor art.
5. Sports: Winnipeg is home to the Winnipeg Jets (NHL) and the Winnipeg Blue Bombers (CFL), and sports are a major part of the city’s identity. There’s a strong sense of community support for local teams, and the games are a big part of the city’s culture.
6. Diversity: The city has a diverse population, with significant Indigenous, Ukrainian, and other immigrant communities contributing to its cultural fabric.
7. Economy: Winnipeg’s economy is diverse, with major sectors including manufacturing, transportation, agriculture, and aerospace. It’s home to several large corporations and offers a mix of urban and industrial landscapes.
IMMIGRATION TO MANITOBA
Immigrating to Manitoba, Canada, is an attractive option for many due to the province’s strong economy, high quality of life, and welcoming communities. Manitoba is known for its diverse population and offers a variety of pathways for immigrants, especially through the Manitoba Provincial Nominee Program (MPNP), which allows skilled workers, entrepreneurs, and family members to apply for permanent residency. Here’s an overview of the key immigration pathways and details about immigrating to Manitoba:
1. Manitoba Provincial Nominee Program (MPNP)
The MPNP is the main immigration route for individuals who wish to live and work in Manitoba. The program has several streams depending on the applicant’s qualifications, skills, and experience:
Skilled Worker Stream
This stream is for skilled workers who have the qualifications and work experience in an occupation that is in demand in Manitoba. It includes:
- Manitoba Skilled Worker Overseas: For individuals who have a connection to Manitoba (e.g., through family, previous work experience, or education in the province) and have the necessary skills for in-demand occupations.
- Manitoba Skilled Worker in Canada: For individuals who are already working in Manitoba with a valid work permit or have an offer of employment from a Manitoba employer.
International Education Stream
This stream is for graduates from a recognized post-secondary institution in Manitoba. Applicants must meet specific eligibility requirements, such as securing a job offer in Manitoba.
Business Investor Stream
This stream is for entrepreneurs and business owners who want to invest in or start a business in Manitoba. There are two subcategories:
- Entrepreneur Pathway: For individuals who intend to establish or buy a business in Manitoba.
- Farm Investor Pathway: For individuals looking to invest in a farming business in the province.
Family Support Stream
Family members of Manitoba residents (Canadian citizens or permanent residents) can apply for immigration under this stream. It requires the sponsor to meet specific criteria.
2. Express Entry System
Manitoba also participates in the Express Entry system, which is managed by Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC). If you meet the requirements of one of the federal economic immigration programs (Federal Skilled Worker Program, Federal Skilled Trades Program, or Canadian Experience Class), you can apply for permanent residency through the Express Entry system. The Manitoba PNP can issue a Manitoba Expression of Interest (EOI) through the Express Entry stream, which will increase your chances of receiving an invitation to apply for permanent residence.
3. Permanent Residency Options
After applying through any of the above pathways, if your nomination is successful, you can apply for permanent residency with IRCC. This usually involves medical and security checks.
4. Other Pathways
- Refugee Resettlement: Manitoba also welcomes refugees who are fleeing conflict, persecution, or violence. The province is home to several resettlement programs and support services to assist newcomers in integrating into the community.
- Temporary Work Permits: Individuals with a job offer in Manitoba can apply for a temporary work permit, which may later lead to permanent residency through the MPNP or Express Entry.
5. Living in Manitoba
Manitoba has a high standard of living and a relatively low cost of living compared to other provinces like Ontario or British Columbia. The province offers:
- A diverse, multicultural environment, especially in cities like Winnipeg, which is the capital and largest city.
- Access to excellent public services, including healthcare, education, and public transportation.
- A vibrant job market with opportunities in various sectors, including manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, and technology.
6. Requirements for Immigration to Manitoba
- Language Proficiency: Depending on the stream, applicants may need to demonstrate proficiency in English or French (e.g., through IELTS or TEF tests).
- Work Experience and Education: Applicants must show that they have the education, work experience, and skills necessary to thrive in Manitoba’s job market.
- Financial Resources: Some immigration streams require proof of sufficient funds to support yourself and your family upon arrival in Manitoba.
7. Settlement Services
Manitoba offers several resources and settlement programs to help immigrants:
- Immigrant-serving organizations: These provide various services like language classes, job search assistance, and cultural integration programs.
- Community support: Manitoba has a strong network of community organizations that assist newcomers with housing, legal advice, and social connections.
- If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
NEW BRUNSWICK
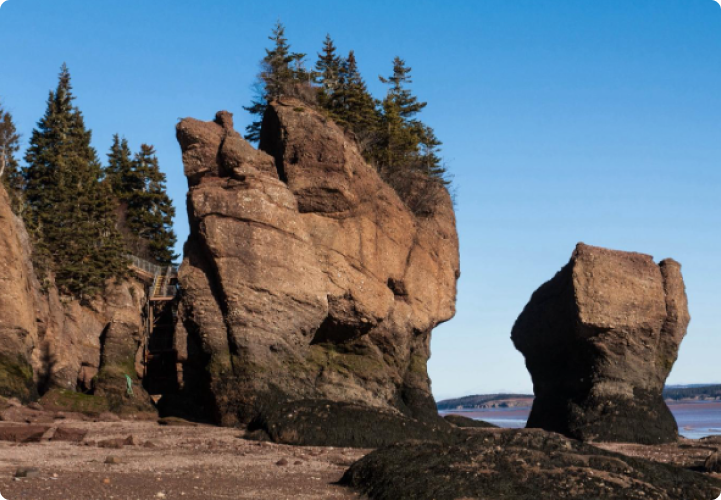

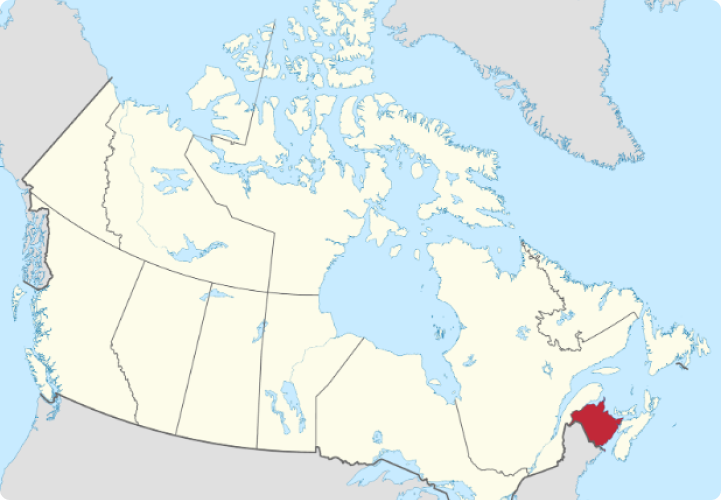


New Brunswick is indeed enchanting and beautiful. The rugged Appalachian Mountain range crisscrosses its North and more than 80% of the Province is covered with thick and lush forests. New Brunswick is the only Canadian province that has two official languages. Both English and Acadian French are official languages in New Brunswick. The early immigrants of New Brunswick were the Mi’kmaq and Maliseet tribes. New Brunswick is a small province, considering the vastness of Canada. Its landmass is about 73,000 square kilometers, and its population less than 800,000, half of whom live in urban areas.
New Brunswick is known for its rich natural landscapes, including forests, rivers, and coastline, as well as its history and cultural diversity.
Here are some key aspects of New Brunswick:
1. Geography
- Capital: Fredericton (located in the central part of the province).
- Largest City: Moncton (a hub for commerce and transportation).
- Other Major Cities: Saint John, which is the oldest incorporated city in Canada and has a significant port.
- Natural Features: The Bay of Fundy, famous for having the highest tides in the world, the Saint John River, and vast forests that make up much of the province’s landscape.
2. History
- Originally inhabited by Indigenous peoples, including the Mi’kmaq and Maliseet, the area now known as New Brunswick was colonized by the French in the early 17th century, part of Acadia.
- After the British gained control of the region in 1713 (Treaty of Utrecht), the population grew, particularly with the arrival of Loyalists fleeing the American Revolution in the late 18th century.
- New Brunswick became a separate colony in 1784, following the American Revolution, when the area was part of the larger Nova Scotia colony.
3. Culture and Languages
- Official Languages: New Brunswick is the only officially bilingual province in Canada, with both French and English being recognized. A significant portion of the population speaks French, particularly in the northern and eastern parts of the province.
- Cultural Influence: New Brunswick has a vibrant Acadian culture, especially in communities like Caraquet, Edmundston, and Dieppe. Acadians, descendants of French settlers, are an integral part of the province’s identity.
- Festivals and Events: The province is known for hosting cultural events like the Harvest Jazz & Blues Festival in Fredericton, and the Acadian Festival in Caraquet.
4. Economy
- Historically, the economy of New Brunswick has been based on natural resources such as forestry, fishing, and agriculture.
- Forestry and Pulp & Paper: The province has large forests, and timber production remains an important sector.
- Fishing: New Brunswick is known for its seafood, particularly lobster, and the Saint John and Shediac regions are major hubs for the fishing industry.
- Energy: The province is also involved in energy production, especially from hydroelectricity, and is exploring renewable energy sources.
5. Tourism and Attractions
- Bay of Fundy: This area is renowned for its spectacular tides and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Fundy Trail Parkway offers scenic views of the coastline.
- Hopewell Rocks: A popular destination where visitors can walk on the ocean floor at low tide and explore the famous rock formations.
- Kouchibouguac National Park: Known for its beautiful beaches, wildlife, and marshlands, it is a great place for outdoor activities.
- Historic Sites: The province is home to many historic sites, such as Kings Landing Historical Settlement, which portrays life in the 19th century, and the city of Saint John, with its historic architecture.
6. Government and Politics
- New Brunswick is governed by a provincial legislature with a premier as the head of government. The current political landscape is shaped by various parties, including the Progressive Conservatives, the Liberals, and the Green Party.
- As part of Canada, it is represented in the federal government, with several members of Parliament in the House of Commons.
7. Climate
- New Brunswick experiences a mix of humid continental and maritime climates, with cold winters and warm, humid summers. Coastal regions tend to be milder in winter but can be very humid in the summer.
8. Education
- New Brunswick has a number of higher education institutions, including the University of New Brunswick (UNB) and Mount Allison University.
New Brunswick is often regarded as a province that offers a quieter lifestyle with plenty of opportunities for outdoor activities and a rich cultural experience, particularly for those who enjoy natural beauty and a mix of English and French heritage.
FREDERICTON
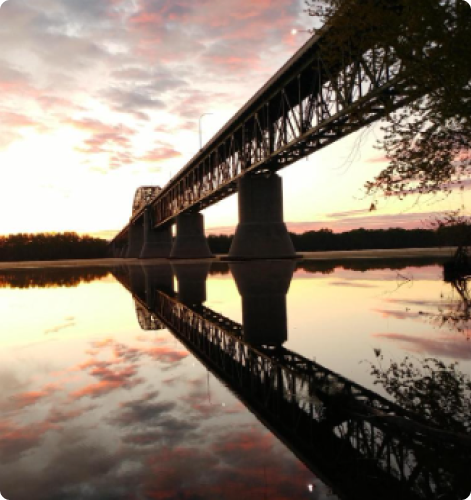



Fredericton is the capital of New Brunswick. Wolastoq River divides Fredericton. This important waterway, which is also known as Saint John River, is a dominant natural feature in the area. The city of Fredericton has a population of about 63,000, which makes it the third largest city in New Brunswick after Moncton and Saint John.
Fredericton has a rich history, charming small-town atmosphere, and vibrant arts and culture scene. Some notable aspects of Fredericton include:
- History: As one of the oldest cities in Canada, Fredericton has a number of heritage sites, including the Christ Church Cathedral and the Old Government House.
- Government: It’s the political hub of New Brunswick, housing the provincial legislature and the offices of the Premier.
- Education: The city is home to the University of New Brunswick (UNB) and St. Thomas University, making it a center for education and research.
- Cultural Scene: Fredericton boasts a number of festivals, including the Fredericton International Film Festival and Folk Festival. The New Brunswick Arts Centre and various galleries contribute to its lively cultural fabric.
- Outdoor Recreation: The city’s location along the Saint John River offers numerous opportunities for outdoor activities like kayaking, cycling, and hiking. There’s also the Odell Park, a large green space for picnics, walks, and outdoor events.
- Climate: Fredericton experiences a humid continental climate, with cold winters and warm summers. Winters are typically snowy, while summers can be quite pleasant.
IMMIGRATION TO NEW BRUNSWICK
Immigration to New Brunswick, a province in eastern Canada, offers several pathways for individuals who wish to live, work, and settle in the region. New Brunswick is known for its rich cultural heritage, scenic landscapes, and welcoming communities. The province has various immigration programs to help skilled workers, entrepreneurs, students, and families immigrate. Below are the main immigration programs and options available for those looking to move to New Brunswick:
1. New Brunswick Provincial Nominee Program (NB PNP)
The New Brunswick Provincial Nominee Program (NB PNP) is designed to attract individuals who have the skills and experience to contribute to the province’s economy. There are several streams under the NB PNP:
- Express Entry Stream: This stream is for candidates who are already in the federal Express Entry pool and have a valid job offer from a New Brunswick employer or have work experience in an occupation that is in demand in the province.
- Skilled Worker Stream: For foreign workers who have a valid job offer from an employer in New Brunswick or those with the skills needed to fill gaps in the provincial labor market.
- Entrepreneurial Stream: Designed for individuals who want to invest in and manage a business in New Brunswick. This stream targets experienced entrepreneurs who can contribute to the local economy.
- International Student Stream: For international students who have completed their studies in New Brunswick and wish to stay and work in the province.
- Family Support Stream: Allows family members of New Brunswick residents to immigrate, provided they meet certain criteria.
2. Atlantic Immigration Program (AIP)
New Brunswick is part of the Atlantic Immigration Program, which was introduced to address labor shortages in the Atlantic provinces (New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland and Labrador). This program focuses on attracting skilled workers and international graduates to the region.
There are three main categories under the AIP:
- Atlantic High-Skilled Program: For skilled workers with a job offer in New Brunswick.
- Atlantic Intermediate-Skilled Program: For workers with a job offer in intermediate-skilled positions.
- Atlantic International Graduate Program: For recent graduates of recognized post-secondary institutions in the Atlantic region with a job offer.
3. Federal Immigration Pathways
Although the provincial programs are a common route, New Brunswick residents can also apply for immigration through federal programs, including:
- Express Entry: Canada’s primary immigration pathway for skilled workers. It is a points-based system that selects candidates based on factors like age, education, work experience, and language proficiency.
- Family Sponsorship: Canadian citizens and permanent residents can sponsor family members, such as spouses, children, or parents, for permanent residency.
4. Start-up Visa Program
New Brunswick also participates in the Start-up Visa Program, which is designed to attract immigrant entrepreneurs who have the skills and potential to establish innovative businesses in Canada. If you want to start a business in New Brunswick, you can apply through this program if you have the support of a designated organization (like a venture capital fund, angel investor group, or business incubator).
5. Temporary Resident Pathways
If you’re looking to work or study in New Brunswick temporarily, you can apply for a temporary work permit or study permit. Many immigrants choose to come to New Brunswick first on a temporary basis, either as international students or temporary foreign workers, and then transition to permanent residency through one of the above pathways.
6. Settlement and Support Services
New Brunswick offers settlement services to help newcomers adjust to life in the province. These services can include assistance with housing, language training, job search support, and community integration.
Key Requirements:
- Language Proficiency: Language skills in English or French (the two official languages of Canada) are often a requirement for most immigration pathways. This can be demonstrated through standardized tests like IELTS (International English Language Testing System) or TEF (Test d’Évaluation de Français).
- Job Offer: For many streams, having a valid job offer from a New Brunswick employer is essential.
- Work Experience/Education: Depending on the program, candidates may need to demonstrate specific work experience or educational qualifications.
Why Choose New Brunswick?
- Affordable Living: Compared to other Canadian provinces, New Brunswick offers a lower cost of living, particularly in terms of housing.
- Quality of Life: The province is known for its beautiful landscapes, including forests, rivers, and coastlines. It has a slower pace of life, making it ideal for individuals and families looking for a quieter environment.
- Economic Growth: New Brunswick is seeing growth in sectors like technology, healthcare, and natural resources, which means there are more job opportunities.
If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR



Newfoundland and Labrador is a province in eastern Canada, consisting of two distinct geographical regions: the island of Newfoundland and the mainland Labrador peninsula. It has a rich history and diverse culture. It is also known for its stunning landscapes, from rugged coastlines to dense forests and barren tundra.
Key Facts about Newfoundland and Labrador:
- Capital: St. John’s (on Newfoundland Island)
- Population: Approximately 520,000 (as of 2021)
- Language: English is the dominant language, but there are also some pockets of French-speaking communities, especially in parts of Labrador.
- Time Zone: Newfoundland Standard Time (NST) or Newfoundland Daylight Time (NDT) in summer, which is unique to the province. It is 30 minutes ahead of the Atlantic Time Zone.
- Geography:
- Newfoundland: The island is the larger part of the province and is known for its rugged coastline, forests, and mountains.
- Labrador: Located on the mainland, Labrador is less populated and known for its vast wilderness, including parts of the Canadian Shield.
History:
- Indigenous Peoples: The region was originally inhabited by Indigenous groups, including the Beothuk, Innu, and Inuit.
- European Exploration: The first European to land in Newfoundland was John Cabot, an Italian explorer under a British flag, in 1497. The island became a key location in the transatlantic fishing industry.
- Colonization: Newfoundland became a British colony in the 17th century, and it remained a self-governing British colony until it joined Canada in 1949.
- Confederation: Newfoundland and Labrador became the 10th province of Canada on March 31, 1949, following a referendum.
Economy:
- Natural Resources: The economy historically relied on the fishing industry (especially cod), but in recent decades, oil and gas exploration in the offshore fields, particularly the Hibernia oil field, have become major economic drivers.
- Tourism: The province attracts tourists with its natural beauty, including Gros Morne National Park (a UNESCO World Heritage Site), the Northern Lights, and the unique culture of coastal communities.
Culture:
- Music and Arts: Newfoundland and Labrador has a vibrant music scene, particularly traditional folk and Celtic music. The province is also known for its unique dialects and rich storytelling traditions.
- Cuisine: Traditional foods include seafood (especially cod), moose, caribou, and “touton” (fried bread). The province has a strong culinary heritage influenced by both its maritime culture and its history of European settlement.
- Festivals: The province hosts numerous festivals celebrating everything from traditional music to arts and theatre.
Interesting Features:
- Signal Hill: Located in St. John’s, Signal Hill is a historical site where Guglielmo Marconi received the first transatlantic wireless signal in 1901.
- Icebergs: The waters off the coast of Newfoundland are famous for being a prime location for iceberg viewing, especially in spring and early summer.
- Newfie Slang: Newfoundland has a rich and distinct vernacular, and local sayings or expressions are often unique to the province. Some popular phrases include “Where y’at?” (How are you?) and “Long may your big jib draw” (A wish for good fortune).
ST. JOHN
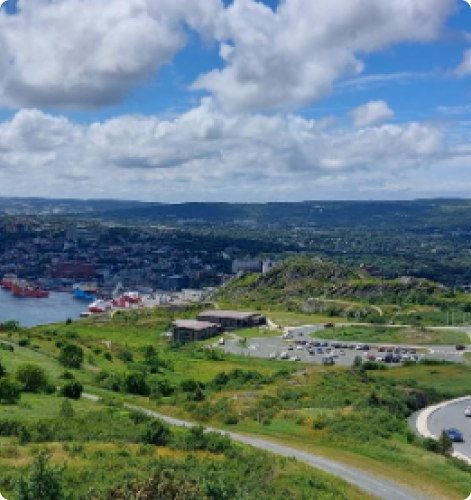
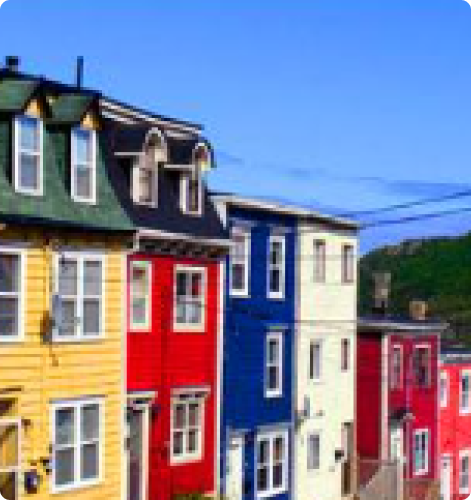
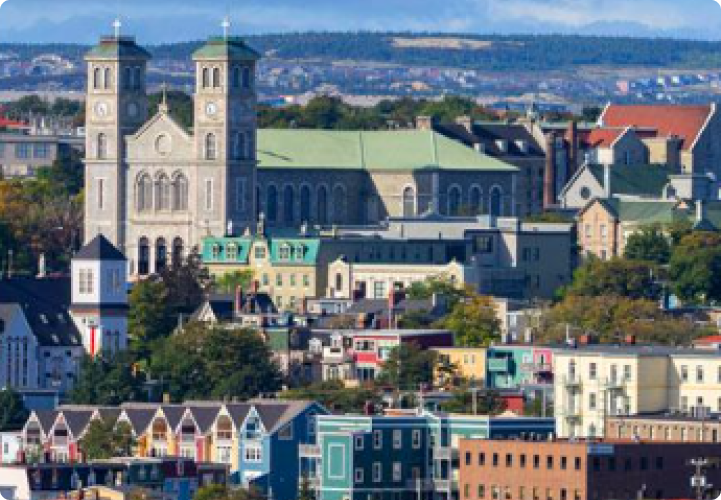








St. John’s is the capital and largest city of Newfoundland and Labrador, a province in eastern Canada. It is one of the oldest European-founded cities in North America, with a rich history that dates back to its founding by John Cabot in 1497. Here are some key details about the city:
1. Geography & Location:
- St. John’s is located on the eastern tip of the Avalon Peninsula on the island of Newfoundland. It lies along the coastline, which is characterized by rugged cliffs and deep harbors.
- The city’s harbor, the St. John’s Harbor, has been crucial for its development and is one of the most prominent natural harbors in North America.
2. History:
- St. John’s was established in the early 1500s and served as a major base for the British and French fisheries. The city’s strategic location made it an important naval port.
- Over the centuries, St. John’s grew through its involvement in transatlantic trade, especially in fish and timber.
- It also played a critical role during the Seven Years’ War and the War of 1812.
3. Culture:
- St. John’s is known for its vibrant arts scene, including music, theater, and visual arts. Traditional Newfoundland folk music is a significant part of the city’s cultural identity.
- The city hosts several festivals throughout the year, including the St. John’s International Women’s Film Festival, the George Street Festival (a celebration of music and nightlife), and the Royal St. John’s Regatta, one of the oldest continuing sporting events in North America.
- The city’s colorful row houses, particularly along Water Street, add to its charm and are a distinctive feature of St. John’s.
4. Landmarks & Attractions:
- Signal Hill: A historic hill that overlooks the city and harbor, where Marconi received the first transatlantic wireless transmission in 1901.
- The Rooms: A modern cultural facility housing art galleries, the Newfoundland and Labrador Archives, and the Provincial Museum.
- Cabot Tower: Situated on Signal Hill, this tower commemorates the 400th anniversary of John Cabot’s landing in North America.
- Quidi Vidi Village: A picturesque area of St. John’s with historic fishing stages and the Quidi Vidi Brewery.
- Cape Spear: The easternmost point in North America, offering breathtaking coastal views.
5. Weather:
- St. John’s has a subarctic climate, characterized by long, cold winters and relatively cool summers. Snow is common during the winter months, and the city often experiences fog, especially in late spring and early summer.
6. Economy:
- Historically, St. John’s was dependent on the fishing industry, but today it is a hub for oil and gas exploration, technology, and tourism. It also serves as a center for government and service industries for the province.
7. Notable Facts:
- George Street: Known for its vibrant nightlife, George Street has more bars and pubs per square meter than anywhere else in North America.
- St. John’s is also known for its warm and friendly people, and the local accent and slang can be quite distinct, often called “Newfoundland English” or “Newfie.”
IMMIGRATION TO NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR
Immigration to Newfoundland and Labrador (NL), the easternmost province of Canada, offers a unique opportunity for individuals seeking to live in a scenic and culturally rich environment. Newfoundland and Labrador is known for its rugged coastlines, rich history, and close-knit communities. The province has several pathways to help immigrants move there, with particular emphasis on skills shortages, economic growth, and population sustainability. Here’s an overview of immigration opportunities and the process:
1. Newfoundland and Labrador Provincial Nominee Program (NLPNP)
The NLPNP is one of the primary pathways for immigrants to move to Newfoundland and Labrador. The program allows the provincial government to nominate individuals who meet the province’s specific labor market needs. It consists of several streams:
- Skilled Worker Stream: For workers with a job offer from an NL employer. Applicants must have the skills, work experience, and education to fulfill the job requirements.
- International Graduate Stream: For graduates from a recognized Newfoundland and Labrador post-secondary institution who have a job offer in the province. The job offer must be related to their field of study.
- Express Entry Skilled Worker Stream: For individuals who are already in the federal Express Entry pool and want to settle in NL. Applicants must have a valid job offer from an NL employer.
- Entrepreneur Stream: For experienced business owners or senior business managers who plan to establish or purchase a business in Newfoundland and Labrador. Applicants must demonstrate the ability to invest and manage a business in the province.
- International Entrepreneur Stream: Aimed at people who have experience in running or managing a business and are looking to start or buy a business in Newfoundland and Labrador. The program requires an investment in the province and the operation of a business.
- Critical Worker Stream: Focused on addressing labor shortages in key sectors like hospitality, food processing, and construction, this stream targets workers in specific high-demand jobs.
2. Express Entry System
Newfoundland and Labrador is aligned with Canada’s Express Entry system, which is a federal program for skilled workers. If you qualify for one of the federal Express Entry categories (Federal Skilled Worker Program, Federal Skilled Trades Program, or Canadian Experience Class), you can apply to be nominated for permanent residence through the NLPNP.
The Express Entry Skilled Worker Stream allows applicants who are already in the Express Entry pool to apply for provincial nomination if they have a job offer from an employer in Newfoundland and Labrador.
3. Atlantic Immigration Program (AIP)
The Atlantic Immigration Program is a federal program designed to attract skilled workers and international graduates to the Atlantic provinces, including Newfoundland and Labrador. The program has three main streams:
- Atlantic High-Skilled Program: For workers with at least one year of work experience in a skilled occupation (NOC 0, A, or B) and a job offer from a designated employer in the province.
- Atlantic Intermediate-Skilled Program: For workers with at least one year of work experience in an intermediate-skilled occupation (NOC C) and a job offer from a designated employer in the province.
- Atlantic International Graduate Program: For international graduates who have studied at a recognized post-secondary institution in one of the Atlantic provinces and have a job offer from a designated employer.
4. Work Permits and Temporary Workers
Newfoundland and Labrador also offers opportunities for temporary workers through various federal work permit programs. The Temporary Foreign Worker Program (TFWP) and International Mobility Program (IMP) allow employers in Newfoundland and Labrador to hire foreign workers to fill labor shortages. Temporary workers can later transition to permanent residency through the NLPNP or other programs.
5. Family Sponsorship
Canada’s Family Sponsorship Program allows Canadian citizens or permanent residents in Newfoundland and Labrador to sponsor their family members, such as spouses, dependent children, parents, or grandparents, for immigration. This is a way to reunite families in the province.
6. Labor Market Opportunities and Key Sectors
Newfoundland and Labrador is focused on attracting skilled workers in various sectors, including:
- Healthcare: Nurses, doctors, and healthcare professionals are in demand.
- Technology and IT: There is a growing tech industry, particularly in software development, digital media, and e-commerce.
- Skilled Trades: There are opportunities in construction, plumbing, electrical work, and other skilled trades.
- Education: Teachers, especially those with experience in specialized fields, are needed.
- Hospitality and Food Services: There is also demand for workers in tourism-related jobs, particularly during peak tourist seasons.
7. Settlement and Support Services
Newfoundland and Labrador has several support services available for immigrants, such as:
- Immigrant and Refugee Support Services: Various community-based organizations assist newcomers with settlement, language support, job placement, and cultural integration.
- Language Training: English as a Second Language (ESL) programs are available to help newcomers improve their language skills.
- Employment Services: Various programs and workshops are available to help immigrants find employment, create resumes, and prepare for job interviews.
8. Cost of Living and Quality of Life
Newfoundland and Labrador offer a relatively affordable cost of living compared to other parts of Canada. The natural environment, cultural diversity, and high quality of life make it an attractive destination for families and individuals. However, due to its geographic location, it can experience cold winters with heavy snowfall.
9. Cultural and Regional Considerations
Newfoundland and Labrador are known for their unique culture, rich history, and close-knit communities. Immigrants can expect a warm, welcoming environment, particularly in smaller communities. The provincial government and local organizations provide programs that help newcomers integrate into the social and cultural fabric of the province.
Newfoundland and Labrador present excellent opportunities for immigration through various streams, particularly for skilled workers, international graduates, entrepreneurs, and those with family connections. The province’s focus on economic growth and addressing labor market gaps means that skilled individuals are in demand, and there is strong support for newcomers to settle and thrive in this scenic and community-oriented part of Canada.
If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
NOVA SCOTIA



Nova Scotia is one of Canada’s 10 provinces, which is located on the Atlantic coast. It is known for its stunning natural beauty, rich history, and vibrant culture. Here are some key facts about Nova Scotia:
Geography
- Location: Nova Scotia is a peninsula, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean on three sides, with the Bay of Fundy to the west and the Gulf of St. Lawrence to the north. It also includes over 3,800 small islands.
- Capital: Halifax, which is the largest city in the province and a major port in Canada.
- Climate: Nova Scotia has a temperate climate with cold winters, warm summers, and significant precipitation throughout the year. Coastal areas experience milder winters compared to the inland regions.
Population and Demographics
- First Nations: The Mi’kmaq people are the original inhabitants of Nova Scotia. The name “Nova Scotia” itself is Latin for “New Scotland,” reflecting the region’s early Scottish settlers.
- French and British Colonialism: Nova Scotia was once part of New France before becoming a British colony in the 18th century. The history of French and British rivalry shaped much of the province’s early development, with famous events like the Expulsion of the Acadians (1755-1763).
- Confederation: Nova Scotia was one of the original provinces of Canada, joining the Confederation on July 1, 1867.
Economy
- Key Industries: Historically, Nova Scotia’s economy has been based on shipbuilding, fishing, forestry, and agriculture. In modern times, it also has a growing tourism industry, particularly thanks to its scenic landscapes, cultural attractions, and maritime heritage.
- Emerging Sectors: Innovation in technology, sustainable energy, and education (with institutions like Dalhousie University) are becoming increasingly important.
Natural Attractions
- Cape Breton Island: Known for its breathtaking landscapes, Cape Breton Island is a popular destination, especially the Cabot Trail, a scenic drive with spectacular coastal views.
- Bay of Fundy: Famous for having the highest tides in the world, the Bay of Fundy is a key feature of the region’s geography.
- National Parks: Nova Scotia boasts several national and provincial parks, including Kejimkujik National Park and Cape Breton Highlands National Park.
Culture
- Music: Nova Scotia has a strong musical tradition, especially folk and Celtic music. The province is known for its fiddling traditions and hosts numerous music festivals.
- Cuisine: Seafood is a central part of the culinary culture, with lobster, mussels, scallops, and fish being staples. Nova Scotia is also famous for its blueberries, apples, and wines (particularly from the Annapolis Valley).
- Festivals and Events: Nova Scotia hosts a variety of festivals celebrating its heritage, such as the Halifax International Busker Festival and the Celtic Colors International Festival in Cape Breton.
Famous Landmarks
- Peggy’s Cove: Known for its iconic lighthouse, Peggy’s Cove is a picturesque fishing village and a popular tourist attraction.
- Fortress of Louisbourg: A National Historic Site, this fortress is a reconstruction of a French colonial town that offers a glimpse into 18th-century life.
- Halifax Citadel: A historic fortress that offers panoramic views of the city and harbor.
Nova Scotia is a province with a rich blend of natural beauty, cultural diversity, and deep historical roots, making it a unique part of Canada. Not to discount the importance of Bras d’Or lake, which is registered with UNESCO as one of the most important wonders of the world.
Bras d’Or Lake is a large inland body of water located on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, Canada. It’s an estuarine lake, meaning it has both saltwater and freshwater influences, as it is connected to the Atlantic Ocean by a series of straits and channels. The lake is renowned for its beauty, diverse ecosystems, and recreational opportunities.

Key Features:
1. Size & Geography: Bras d’Or Lake covers an area of about 1,000 square kilometers (400 square miles) and has a complex, irregular shoreline with several peninsulas, islands, and coves.
2. Water Composition: The lake is partially saltwater due to its connection to the ocean. It’s known for its brackish water, which creates a unique environment for a variety of plant and animal species.
3. Historical Significance: The name “Bras d’Or” is French for “Arm of Gold,” and it was given by early French explorers. The lake has long been important to the indigenous Mi’kmaq people and later to European settlers for transportation, trade, and settlement. It also played a significant role in the development of Cape Breton’s economy, particularly in shipbuilding.
4. Ecology: The lake supports a variety of wildlife, including fish species like Atlantic salmon, striped bass, and rainbow trout. It also has rich birdlife, including waterfowl and migratory birds. The surrounding forests are home to many terrestrial species.
5. Recreation: The lake is popular for recreational activities such as boating, kayaking, fishing, and swimming. The surrounding area offers hiking trails, wildlife watching, and camping.
6. Bras d’Or Lakes Scenic Drive: This is a popular route that circles the lake and offers spectacular views of the surrounding landscape, including the rugged coastline, forests, and charming coastal communities.
7. Cultural Significance: The lake continues to be important to the local Mi’kmaq people and has cultural and spiritual significance. The area around the lake is also home to several small communities and offers visitors a glimpse into rural Cape Breton life.
HALIFAX



Halifax is the capital of Nova Scotia. Located on the Atlantic coast, it’s a major economic and cultural hub in the region. Halifax is also known for its rich maritime history, vibrant arts scene, and beautiful coastal landscapes. Here are a few key things about Halifax:
1. Historical Significance:
- Halifax has a deep maritime history. It was founded in 1749 by the British as a strategic military and naval base.
- The city is known for the Halifax Explosion of 1917, one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in history, when a munitions ship collided with another vessel in the harbor.
- Pier 21, now a museum, was the main point of entry for over a million immigrants to Canada from 1928 to 1971.
2. Geography:
- Situated on the Halifax Harbor, the city is known for its waterfront and picturesque views. The harbor is one of the largest in the world, making it an important location for trade and shipping.
- The city is surrounded by natural beauty, with many parks, forests, and beaches nearby.
3. Cultural and Educational Hub:
- Halifax is home to a number of institutions, including Dalhousie University, Saint Mary’s University, and Mount Saint Vincent University, making it a key center for higher education.
- The city has a lively arts scene, with numerous festivals, theaters, and galleries. The Halifax International Busker Festival and Halifax Pop Explosion are major annual events.
4. Tourism:
- The city boasts several historical sites like Citadel Hill, Alexander Keith’s Brewery, and the Maritime Museum of the Atlantic.
- Peggy’s Cove, a famous lighthouse located just outside the city, is a popular tourist destination, known for its scenic views.
- Point Pleasant Park and Halifax Public Gardens offer beautiful green spaces in the heart of the city.
5. Economy:
Halifax is a key player in Canada’s maritime economy. The Port of Halifax is one of the busiest in the country.
The city also has a strong presence in industries such as defense, technology, and finance, with several companies and government organizations based there.
Halifax’s blend of historical charm, coastal beauty, and modern amenities makes it a distinctive and attractive city to live in or visit.
IMMIGRATION TO NOVA SCOTIA
Immigrating to Nova Scotia, Canada, involves several steps, and there are various pathways to do so depending on your qualifications, skills, and intentions. Nova Scotia is a province with a high quality of life, scenic beauty, and a welcoming community, which makes it an attractive destination for immigrants. Here’s an overview of the immigration options and process for moving to Nova Scotia.
1. Express Entry
The Express Entry system is Canada’s primary way of managing applications for permanent residence from skilled workers. Nova Scotia has a Provincial Nominee Program (PNP) that allows the province to nominate candidates from the federal Express Entry pool. The two key Express Entry streams relevant to Nova Scotia are:
- Federal Skilled Worker Program: For skilled workers with relevant work experience and education.
- Federal Skilled Trades Program: For workers with experience in skilled trades.
- Canadian Experience Class: For candidates with Canadian work experience.
Nova Scotia regularly conducts labor market assessments and nominates candidates based on the province’s needs. Candidates in the Express Entry pool who meet Nova Scotia’s criteria can receive a provincial nomination, which adds 600 points to their Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) score, effectively guaranteeing an invitation to apply for permanent residency.
2. Nova Scotia Provincial Nominee Program (NS PNP)
The NS PNP allows Nova Scotia to nominate individuals who want to live and work in the province. The program offers several streams, including:
- Skilled Worker Stream: For workers who have a job offer from a Nova Scotia employer.
- International Graduate Stream: For recent graduates from a recognized post-secondary institution in Nova Scotia with a job offer.
- Entrepreneur Stream: For individuals who want to start or buy a business in Nova Scotia. This stream requires a business plan and investment.
- Labor Market Priorities Stream: For candidates with skills or experience in high-demand occupations. The province occasionally conducts targeted recruitment based on labor market needs.
- Nova Scotia Demand: Express Entry Stream: This stream is aligned with the federal Express Entry system. The province nominates individuals who have skills or qualifications in occupations where there is a labor shortage.
3. Atlantic Immigration Program (AIP)
The Atlantic Immigration Program is designed to attract and retain skilled workers and international graduates to the four Atlantic provinces, including Nova Scotia. It is employer-driven, meaning that you need a job offer from a designated employer in Nova Scotia to apply through this program. It has the following streams:
- Atlantic High-Skilled Program: For workers with experience in managerial, professional, or technical jobs.
- Atlantic High-Skilled Program: For workers with experience in managerial, professional, or technical jobs.
- Atlantic International Graduate Program: For international graduates who have studied in one of the Atlantic provinces and have a job offer from a designated employer.
4. Study Permits (for International Students)
Nova Scotia is home to several world-class universities and colleges, such as Dalhousie University and Saint Mary’s University. If you are an international student, you can apply for a study permit to study in Nova Scotia. After completing your studies, you may be eligible to apply for a Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP), which allows you to work in Canada for up to three years.
After gaining work experience, you may be able to transition to permanent residency through one of the streams mentioned above, such as the Canadian Experience Class or the Nova Scotia PNP International Graduate Stream.
5. Family Sponsorship
If you have a family member who is a Canadian citizen or permanent resident living in Nova Scotia, they may be able to sponsor you for permanent residency. This program includes:
- Spouse or Common-Law Partner Sponsorship
- Parent and Grandparent Sponsorship
- Dependent Child Sponsorship
The sponsor must meet specific eligibility requirements, and you must demonstrate that the relationship is genuine.
6. Temporary Work Permits
If you have a job offer from an employer in Nova Scotia, you can apply for a temporary work permit. While this does not lead directly to permanent residency, it allows you to live and work in the province temporarily and may offer a pathway to permanent residency later if you gain Canadian work experience or are nominated through one of the immigration streams.
7. Start-Up Visa Program
The Start-Up Visa Program is for entrepreneurs who want to establish a business in Canada and create jobs. You will need to secure a commitment from a designated organization (such as a venture capital fund or angel investor) that will support your business idea. If your business is successful, this could lead to permanent residency.
8. Rural and Northern Immigration Pilot (RNIP)
Nova Scotia participates in the Rural and Northern Immigration Pilot, which allows certain smaller communities to nominate skilled workers for permanent residence. The program focuses on bringing workers to rural and northern communities that have specific labor shortages.
9. Eligibility Requirements
Regardless of the immigration stream, you must meet certain eligibility criteria, which may include:
- A valid job offer and sufficient work experience.
- Proof of financial stability (e.g., funds to support yourself and your family).
- Language proficiency in English or French (through tests such as IELTS or TEF).
- Educational credentials and qualifications (sometimes verified through the Educational Credential Assessment (ECA)).
Application Process Overview:
1. Determine Eligibility: Check which immigration stream fits your qualifications and circumstances.
2. Gather Documents: Prepare documents such as language test results, educational credentials, work experience, proof of funds, and job offers.
3. Submit Expression of Interest (EOI): For some streams (like the NS PNP), you will need to submit an EOI to express your interest in being nominated.
4. Receive Nomination or Invitation: If you are nominated by Nova Scotia or invited to apply, submit your permanent residency application to Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada (IRCC).
5. Wait for Processing: The processing times vary depending on the program but typically range from a few months to a year or more.
6. Receive Permanent Residency: If your application is successful, you will be granted permanent residency, allowing you to live and work in Nova Scotia.
Nova Scotia offers a range of immigration pathways depending on your background and qualifications. Whether you’re a skilled worker, entrepreneur, international student, or a family member seeking to reunite with loved ones, there are several options available to help you settle in this beautiful and thriving province.
If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND
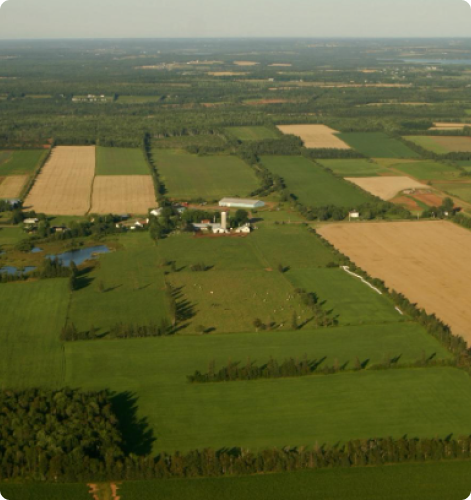
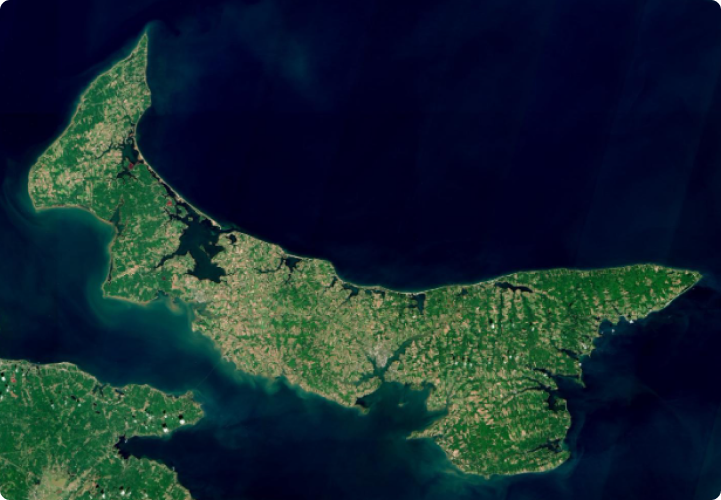

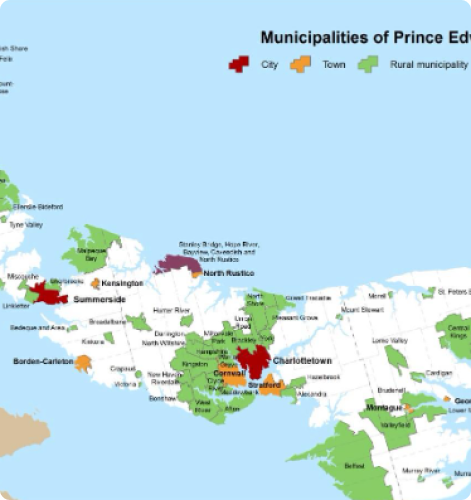


Prince Edward Island (PEI) is located in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. It is the smallest of Canada’s ten provinces in both area and population, but it holds a special place in Canadian history and culture. Here are some key things to know about PEI:
Geography
- Location: PEI is an island province situated to the east of mainland Canada, off the coast of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Quebec.
- Size: It has an area of about 5,660 square kilometers (2,190 square miles), making it the smallest province in Canada by land area.
- Climate: The island experiences a temperate climate with relatively mild winters and cool summers. Coastal weather can change quickly due to its proximity to the ocean.
History
- Confederation: PEI was the last of the original British colonies to join Canada. It became a province on July 1, 1873, after initially rejecting the terms of Confederation in 1867.
- First Nations: Before European settlers arrived, the island was inhabited by the Mi’kmaq people for thousands of years. The Mi’kmaq still have a presence on the island today.
Culture & Economy
- Tourism: PEI is famous for its natural beauty, charming villages, and historic sites. Tourism is a major industry, with visitors drawn to the island’s red sandstone cliffs, sandy beaches, and rolling countryside.
- Agriculture: PEI is known for its agricultural products, especially potatoes. The island is a leading producer of potatoes in Canada, and its fertile soil supports many other crops.
- Lobster: Fishing, particularly lobster fishing, is another important part of the economy. PEI lobster is a sought-after delicacy worldwide.
- Anne of Green Gables: The island is perhaps most famous for being the setting of L.M. Montgomery’s Anne of Green Gables. The story of Anne, a fictional orphan girl, is beloved internationally, and the Anne-themed sites, including the Green Gables house, attract many visitors.
Population and Language
- Population: PEI has a relatively small population of about 160,000 people (as of 2021). The capital city is Charlottetown, which is also the largest city on the island.
- Population: PEI has a relatively small population of about 160,000 people (as of 2021). The capital city is Charlottetown, which is also the largest city on the island.
Transportation
- Confederation Bridge: This iconic bridge connects PEI to the mainland of New Brunswick. Opened in 1997, it is one of the longest bridges in the world over ice-covered waters.
- Ferries: Ferries also operate between PEI and the mainland, offering another way for travelers to reach the island.
Attractions
- Prince Edward Island National Park: A scenic park known for its beautiful beaches, dunes, and historic sites.
- The Confederation Centre of the Arts: A cultural venue in Charlottetown that hosts the musical Anne of Green Gables and other performances.
- PEI’s lighthouses: The island is home to many picturesque lighthouses, with several open to the public for tours.
PEI is often described as Canada’s “gentle island” for its relaxed pace of life, beautiful natural scenery, and close-knit communities. Whether you’re visiting for the stunning landscapes, rich history, or the enduring legacy of Anne of Green Gables, PEI offers a distinctive and memorable experience.
CHARLOTTETOWN


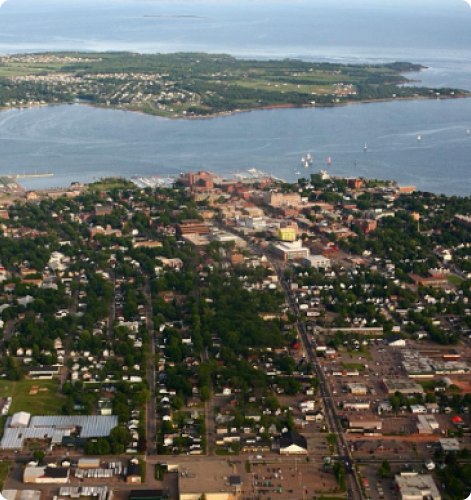
Charlottetown is the capital city of Prince Edward Island (PEI), Canada. Located on the island’s southern coast, it’s often referred to as the “Birthplace of Confederation” because it was the site of the 1864 Charlottetown Conference, where discussions took place that led to the creation of Canada as a country in 1867.
Here are a few key highlights about Charlottetown:
History
- The city was established in 1765 and named after Queen Charlotte, the wife of King George III.
- Charlottetown played a central role in the creation of Canada, as the 1864 conference was a critical moment in the country’s founding. Delegates from various British colonies met to discuss the possibility of uniting into one dominion, which would later become Canada.
Cultural Significance
- Charlottetown is known for its vibrant arts scene. It’s home to the Confederation Centre of the Arts, a major venue for performing arts, including musical theater and visual arts. The musical Anne of Green Gables is famously staged there, inspired by the novel by L.M. Montgomery, who lived in PEI.
- The city is also known for its historic architecture, particularly in the downtown area, where many buildings date back to the 19th century.
Geography and Climate
- Location: Situated on the southern shore of PEI, Charlottetown has a picturesque harbor and is surrounded by scenic landscapes, including beaches, forests, and farmland.
- Climate: The city has a maritime climate, with cold winters and mild, humid summers. Snow and ice can be common during winter months, while summers are generally pleasant, attracting tourists.
Economy
- The economy of Charlottetown is diverse, with sectors such as government, tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing contributing to its growth. The tourism industry is especially significant, with many visitors coming to explore the history, natural beauty, and cultural events.
Population and Demographics
As of the last census, Charlottetown had a population of around 40,000 people, though it is part of a larger metropolitan area. The city serves as a hub for business, government, and education for the island.
Notable Landmarks
- Province House: This is where the Charlottetown Conference took place in 1864 and is now a National Historic Site. It’s still used for the Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island.
- Victoria Park: A beautiful, well-maintained park along the waterfront, ideal for walking, picnicking, or enjoying outdoor events.
- Peake’s Wharf: A bustling waterfront area offering shops, restaurants, and attractions with a view of the harbor.
IMMIGRATION TO PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND (PEI)
Immigrating to Prince Edward Island (PEI), Canada, offers a variety of opportunities for individuals looking to settle in one of the most picturesque provinces in the country. PEI is known for its small-town charm, strong agricultural sector, and growing economy. If you’re interested in immigrating to PEI, here’s an overview of the pathways and considerations:
1. Prince Edward Island Provincial Nominee Program (PEI PNP)
The PEI PNP is a popular route for skilled workers, entrepreneurs, and individuals with close family ties to the island. There are several streams under the PEI PNP:
- Express Entry Stream: For candidates who are already in the federal Express Entry pool. This stream targets skilled workers who have the qualifications and experience to meet the demands of PEI’s labor market.
- Labor Impact Category: This is for workers who have a valid job offer from a PEI employer. It includes streams like Skilled Worker, Critical Worker, and International Graduate streams, depending on the applicant’s work experience and educational background.
- Business Impact Category: For individuals interested in investing and starting or purchasing a business in PEI. There are streams like the Entrepreneur Stream and Work Permit Stream.
- Family Stream: For individuals who have close family members (such as parents, children, or siblings) who are residents of PEI and want to support your immigration process.
2. Federal Immigration Programs
In addition to the PEI PNP, there are federal immigration programs you can apply through, including:
- Express Entry: A federal program for skilled workers, which is often linked to the PEI PNP. Express Entry candidates can apply directly through the federal system, or they may receive a provincial nomination from PEI for additional points toward their Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) score.
- Atlantic Immigration Program (AIP): This is a specific program for the Atlantic provinces (including PEI) that helps skilled workers, international graduates, and their families move to PEI. The AIP is employer-driven, meaning a job offer is typically required.
- Family Sponsorship: If you have a close family member who is a Canadian citizen or permanent resident, they can sponsor you for permanent residence in Canada.
3. Study Pathway
If you are a student, studying in PEI can be a pathway to permanent residency through the Atlantic Immigration Program or PEI PNP. Graduates from recognized institutions in PEI may be eligible for work permits and permanent residency if they secure a job in the province.
4. Job Market and Economy
PEI’s economy is mainly based on agriculture, tourism, and fishing. Recent economic diversification has included growing sectors like technology, healthcare, and manufacturing. Some sectors experiencing demand for skilled workers include:
- Healthcare professionals
- Construction and trades
- Information technology (IT) professionals
- Agricultural workers
- Tourism-related positions
5. Living in Prince Edward Island
- Cost of Living: PEI has a relatively lower cost of living compared to other provinces like Ontario or British Columbia. Housing, food, and healthcare are affordable, making it a great place for families to settle.
- Community and Lifestyle: Known for its beautiful beaches, green landscapes, and laid-back lifestyle, PEI is an excellent place for those who enjoy outdoor activities like hiking, boating, and farming.
- Support for Immigrants: There are various settlement services available for newcomers, including language classes, job placement assistance, and community integration programs.
6. How to Apply
- You must meet eligibility requirements for one of the PEI immigration streams or federal programs.
- If applying under the PEI PNP, you will need to submit an application to the province for a nomination.
- Once nominated, you can apply to the federal government for permanent residence.
If you are considering immigrating to anywhere in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
SASKATCHEWAN

Saskatchewan is a province in central Canada, known for its vast prairies, forests, and agricultural industry, especially the vast wheat fields. Here are some key facts about Saskatchewan:
Geography
- Location: Saskatchewan is bordered by Alberta to the west, Manitoba to the east, and the US states of Montana and North Dakota to the south.
- Landscape: The province is made up of prairie grasslands, boreal forests, and a number of lakes and rivers, including the Saskatchewan River, which runs through the province.
Economy
- Agriculture: Saskatchewan is one of Canada’s most important agricultural regions, particularly for crops like wheat, canola, and barley. It also has a significant cattle industry.
- Natural Resources: The province is a major producer of potash, uranium, and oil. It also has extensive forestry resources.
- Mining: Saskatchewan is a global leader in the production of potash (used in fertilizer), and it has large deposits of uranium.
Climate
- Type: Saskatchewan experiences a continental climate with cold winters and warm summers. It is known for its extreme temperature changes and can have long, harsh winters with heavy snowfall and high winds.
Population and Major Cities
- Population: The population of Saskatchewan is around 1.2 million people, with the majority living in urban centers.
- Regina: The capital city of Saskatchewan, located in the southern part of the province, is known for its government buildings, cultural institutions, and as the home of the Saskatchewan Roughriders, a Canadian football team.
- Saskatoon: The largest city in Saskatchewan, located in the central part of the province. It is a hub for innovation, technology, and education, with the University of Saskatchewan based there.
Culture and Tourism
- Indigenous Peoples: Saskatchewan is home to many Indigenous communities, including the Cree, Dene, Nakoda, and Saulteaux peoples. Indigenous culture is an integral part of the province’s heritage.
- Nature and Outdoors: Saskatchewan is popular for outdoor activities such as hiking, fishing, boating, and snowmobiling. The province is also home to many provincial parks and nature reserves.
- Tourism: People often visit Saskatchewan to experience its natural beauty, from the plains to the boreal forests, as well as its rich cultural festivals, including the Saskatoon Fringe Festival and the Regina Folk Festival.
REGINA



Regina is the capital city of Saskatchewan, and it is located in the southern part of the province. It sits on the Trans-Canada Highway and is known for its beautiful parks, vibrant arts scene, and rich cultural history. The city is also the home of the Saskatchewan Roughriders, the province’s beloved Canadian football team.
A few highlights about Regina:
- History: Regina was established in 1882 as a rail town and was named after Queen Victoria. It became the provincial capital in 1905 when Saskatchewan became a province.
- Government and Education: Regina is a center for the provincial government and hosts the University of Regina, which is known for its research and academic programs.
- Landmarks:
- Wascana Centre: A massive park and recreational area with a lake, walking paths, museums, and gardens.
- Royal Saskatchewan Museum: Features exhibits on the natural and cultural history of the province.
- Mosaic Stadium: The home stadium of the Saskatchewan Roughriders, where fans gather to watch Canadian football games.
Regina also hosts various festivals and events throughout the year, such as the Regina Folk Festival and the Queen City Ex, which is an annual fair featuring entertainment, food, and rides.
IMMIGRATION TO SASKATCHEWAN
Immigrating to Saskatchewan, a province in Canada, is an appealing option for many individuals due to its strong economy, scenic landscapes, and quality of life. Saskatchewan offers several pathways for immigration, including programs for skilled workers, entrepreneurs, and family members. Here are the main options for immigrating to Saskatchewan:
1. Saskatchewan Immigrant Nominee Program (SINP)
The SINP is the primary immigration program through which individuals can immigrate to Saskatchewan. It allows the province to nominate individuals for permanent residence based on the needs of the local labor market. The SINP is divided into several categories:
Skilled Worker Category
- International Skilled Worker (ISW) Subcategory: For individuals with a job offer in Saskatchewan or those who meet the requirements of the province’s labor market.
- Express Entry Subcategory: For candidates already in the federal Express Entry pool. It selects candidates based on factors such as age, education, work experience, and language proficiency.
- Occupation In-Demand Subcategory: For skilled workers who do not have a job offer but possess experience in an occupation that is in demand in Saskatchewan.
- Royal Saskatchewan Museum: Features exhibits on the natural and cultural history of the province.
Saskatchewan Experience Category
This category is for individuals who are already living and working in Saskatchewan under temporary work permits. It includes the following subcategories:
- Existing Work Permit: For individuals with a valid job offer and who have worked in Saskatchewan for at least six months.
- Health Professionals: For workers in healthcare occupations.
- Hospitality Workers: For individuals working in the hospitality industry.
Entrepreneur and Farm Category
- Entrepreneur Subcategory: For individuals who want to start a business in Saskatchewan.
- Farm Owner and Operator Subcategory: For individuals who want to operate a farm in Saskatchewan.
Family and Friends Category
For individuals who have close family members who are permanent residents or citizens of Saskatchewan, they may be able to sponsor their relatives through this category.
2. Federal Express Entry System
If you’re eligible for the Express Entry system (the federal system for skilled workers), you can be invited to apply for permanent residency in Canada. If you are nominated by Saskatchewan through the SINP Express Entry stream, you’ll receive additional points toward your Express Entry Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) score, improving your chances of receiving an Invitation to Apply (ITA) for permanent residence.
3. Temporary Work Permits and Job Offers
For those who wish to come to Saskatchewan temporarily, securing a job offer from a Saskatchewan employer can be an important step. Temporary work permits can lead to permanent residency through the SINP or other federal immigration programs.
4. Studying in Saskatchewan
International students who graduate from recognized institutions in Saskatchewan may be eligible to apply for a Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP). After gaining work experience, they may apply for permanent residency through programs like the SINP or Express Entry.
5. Living in Saskatchewan
Once you settle in Saskatchewan, you’ll be able to enjoy:
- Affordable cost of living compared to larger provinces like Ontario and British Columbia.
- A strong economy, with opportunities in sectors like agriculture, mining, energy, and technology.
- High quality of life with excellent healthcare, education, and recreational activities.
- Cultural diversity, with a growing community of immigrants.
Eligibility Requirements:
To apply through the SINP or federal programs, you’ll typically need to meet specific criteria:
- Education: Typically, a minimum of a high school diploma or higher is required, and for skilled workers, a degree or diploma in a relevant field.
- Work experience: Certain programs require specific work experience in demand by the province.
- Language proficiency: Applicants need to prove proficiency in English or French, typically via an approved language test (e.g., IELTS for English).
- Health and security: You will need to pass medical and security checks to qualify for Canadian permanent residency.
As you can see, Saskatchewan provides various immigration pathways for skilled workers, entrepreneurs, students, and individuals with family ties in the province. The province offers a good balance of economic opportunity, natural beauty, and affordability. If you are considering immigrating to Saskatchewan or any other location in Canada, please Click or Call Chosen Canadian Immigration Lawyers and let them help you realize your dreams safely and soundly.
REQUEST A FREE CASEEVAL UATION
Together, We Can Turn Your Immigration Dreams into Realities!